Elsevier, Biological Conservation, Volume 245, May 2020
If moral concern for nonhuman nature underpins conservation, it is essential to understand how individuals populate their “moral communities,” a core concept from environmental ethics, with various elements of biodiversity. Using data from an online survey of the United States public (N = 1331), we investigated the extent to which respondents' moral communities align with four worldviews discussed in the environmental ethics literature: anthropocentrism, zoocentrism, biocentrism, and ecocentrism. Each worldview provides a vision for how the moral community should be constituted.
Elsevier, Biological Conservation, Volume 245, May 2020
Refuges and refugia are important to conservation management because of their potential to protect species from difficult-to-manage threats such as changing climate, extreme events (e.g., drought, fire) and biotic threats (e.g., disease, invasive species). To provide conservation managers with an evidence-based approach to identifying refuges and refugia, we ask: which places have been observed to function as refuges/refugia, with results reported in the scientific literature? We systematically reviewed the past 20 years of research into refuges/refugia.
Elsevier, Journal of Neuroscience Methods, Volume 337, 1 May 2020
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and is a serious health problem. The disease is expected to increase further in the upcoming years with the increase of the elderly population. Developing new treatments and diagnostic methods is getting more important. In this study, we focused on the early diagnosis of dementia in Alzheimer's disease via analysis of neuroimages. We analyzed the data diagnosed by the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) protocol.
Elsevier, EClinicalMedicine, Volume 22, May 2020
Background: In Niger the prevalence of girl child marriage and low female control over family planning (FP) has resulted in the world's highest adolescent fertility. Male control of FP is associated with intimate partner violence (IPV) and reproductive coercion (RC). We assessed associations of IPV and RC with FP use among married adolescent girls (ages 13–19 years) in Dosso, Niger (N = 1072).
Elsevier, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 135, May 2020
Improving bus stops by providing shelters, seating, signage, and sidewalks is relatively inexpensive and popular among riders and local officials. Making such improvements, however, is not often a priority for U.S. transit providers because of competing demands for capital funds and a perception that amenities are not tied to measurable increases in system effectiveness or efficiency.
Elsevier, Catena, Volume 188, May 2020
This study investigates the ostracod assemblages obtained from a sediment core from a paleolake in the Sağlık plain in south-central Anatolia (Turkey). In addition to ostracods, oxygen and. carbon stable isotopes of ostracod shells were analysed and pollen analysis of the core undertaken. The sediments comprise the Late Glacial and early Holocene interval with an approximate 14C age from 18,000 to 6700 14C years ago, after applying a correction for reservoir effects. Eight podocopid ostracod species were recorded, among them Cyprideis torosa and Candona sp.
Elsevier, Agricultural Water Management, Volume 235, 31 May 2020
Climate change and population growth generates a decrease in water availability around the world which can compromise the maintenance of sustainable agriculture. Thus, treated wastewater (TWW) became an alternative to minimize water shortage. However, this may indirectly affect the soil's microbial properties. In this study different soils irrigated for 0, 1, 8 and 20 years with TWW were sampled and from the east central region of Tunisia.
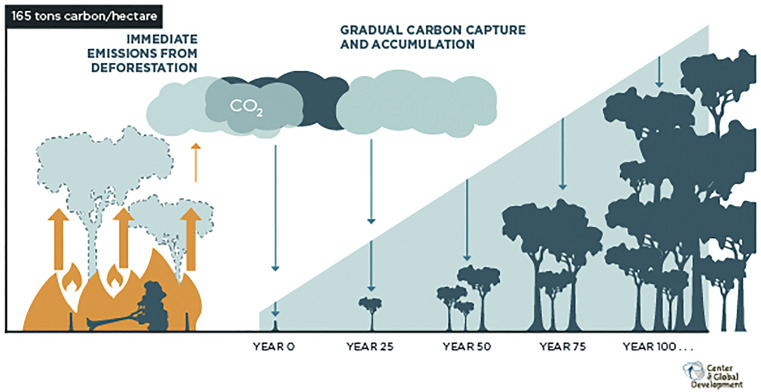
Elsevier, One Earth, Volume 2, 22 May 2020
Largely driven by the corporate sector, the recent surge of interest in trees as a solution to climate change has a distinct emphasis on planting trees. Realizing anticipated benefits will require managing the risks and trade-offs of land-use interventions and embracing the imperative of protecting existing forests.
Elsevier, One Earth, Volume 2, 22 May 2020
Forests are key components of the global carbon cycle and dominate mitigation strategies for climate change and biodiversity loss. In contrast, the importance of and threats facing ocean forests—kelp forests—are comparatively underappreciated. Yet, increasing the global area of kelp forests would enhance biodiversity and drawdown CO2, mitigating climate change.