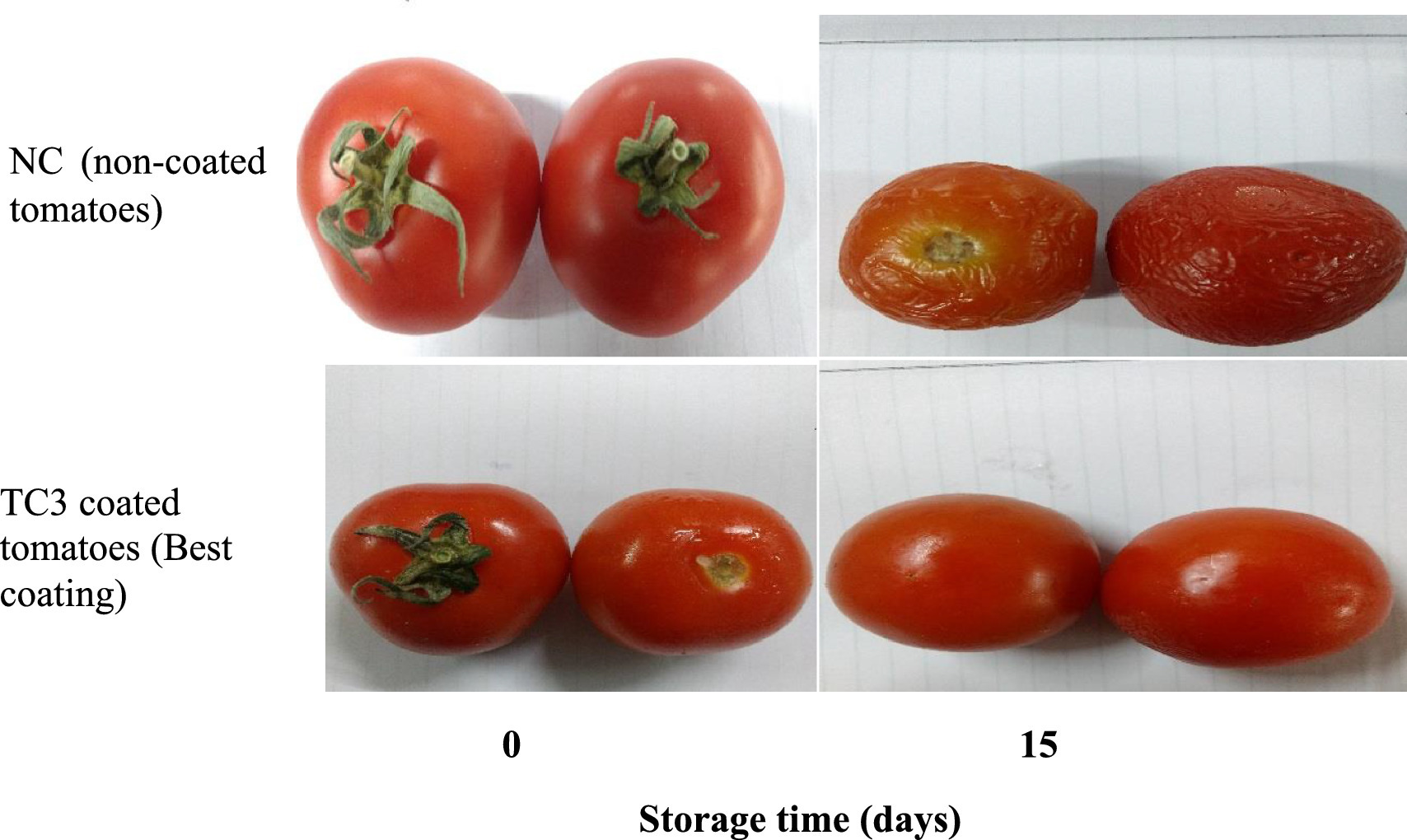
Elsevier,
CJC Open, Volume 3, December 2021
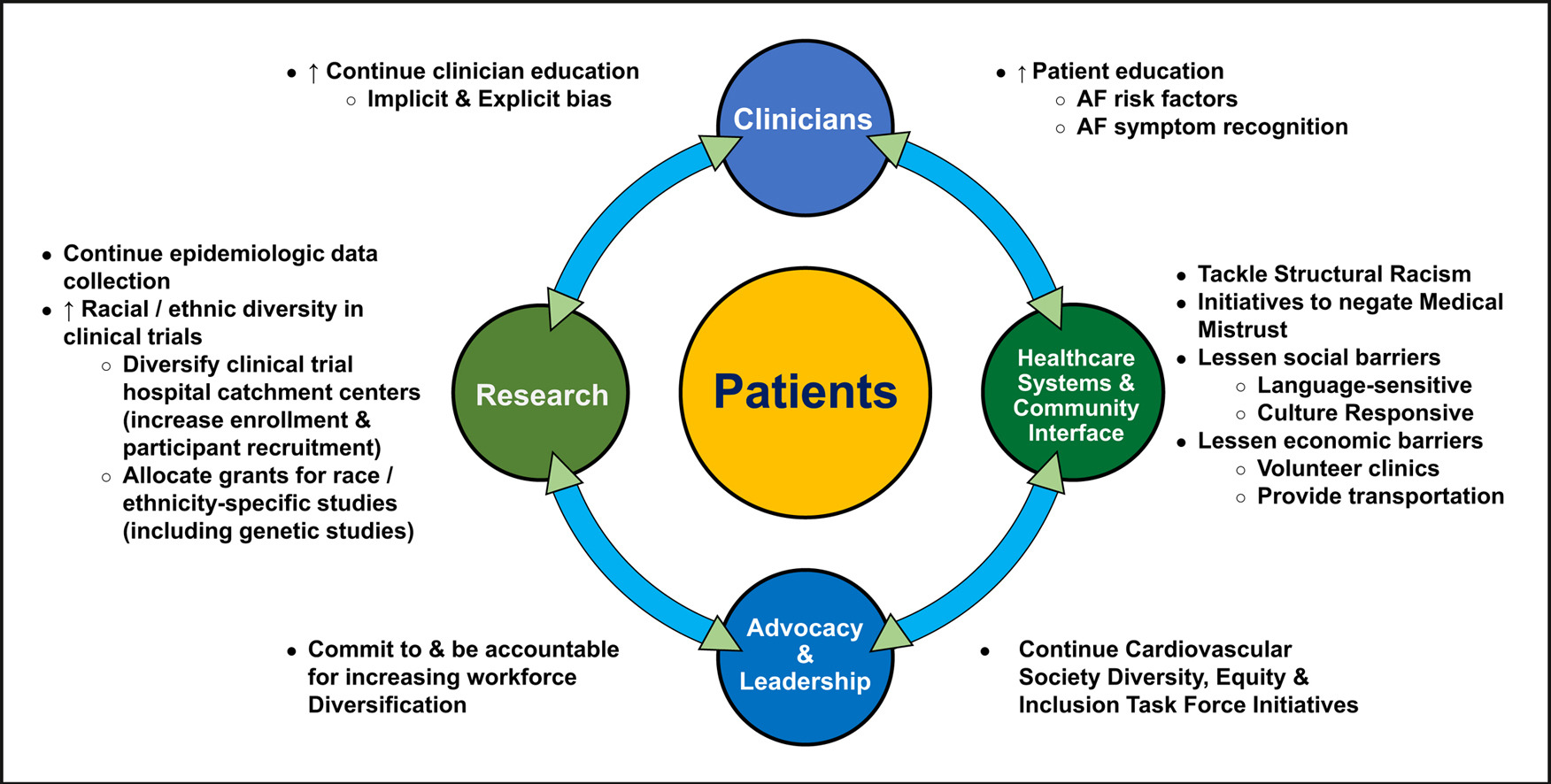
This article highlights the underrepresentation of racial and ethnic populations in atrial fibrillation clinical trials, especially trials focused on stroke prevention. Specific strategies are proposed for future research and initiatives that have potential to eliminate racial and ethnic differences in the care of patients with atrial fibrillation.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 3, 2021, 100074
Correspondence on the factors behind low COVID-19 immunisation coverage among marginalised communities in Latin America and the Caribbean, in the context of SDGs 3 and 10, highlighting the need to consider the specific circumstances of Indigenous communities in the development of national COVID-19 immunisation campaigns.
Elsevier,
Energy and AI, Volume 5, September 2021
This article supports SDGs 7 and 9 by introducing interpretable artificial intelligence (AI) tools, especially proxy models based on artificial neural networks, efficient variable analysis and optimal value prediction of membrane electrode components in proton exchange membrane fuel cells, thereby improving their performance and reducing computational costs.
Elsevier,
Redox Biology, Volume 45, September 2021
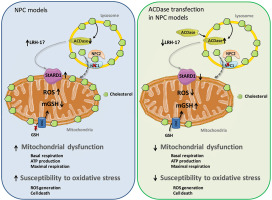
Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease, a lysosomal storage disorder caused by defective NPC1/NPC2 function, results in the accumulation of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in lysosomes of affected organs, such as liver and brain. Moreover, increase of mitochondrial cholesterol (mchol) content and impaired mitochondrial function and GSH depletion contribute to NPC disease. However, the underlying mechanism of mchol accumulation in NPC disease remains unknown. As STARD1 is crucial in intramitochondrial cholesterol trafficking and acid ceramidase (ACDase) has been shown to regulate STARD1, we explored the functional relationship between ACDase and STARD1 in NPC disease.