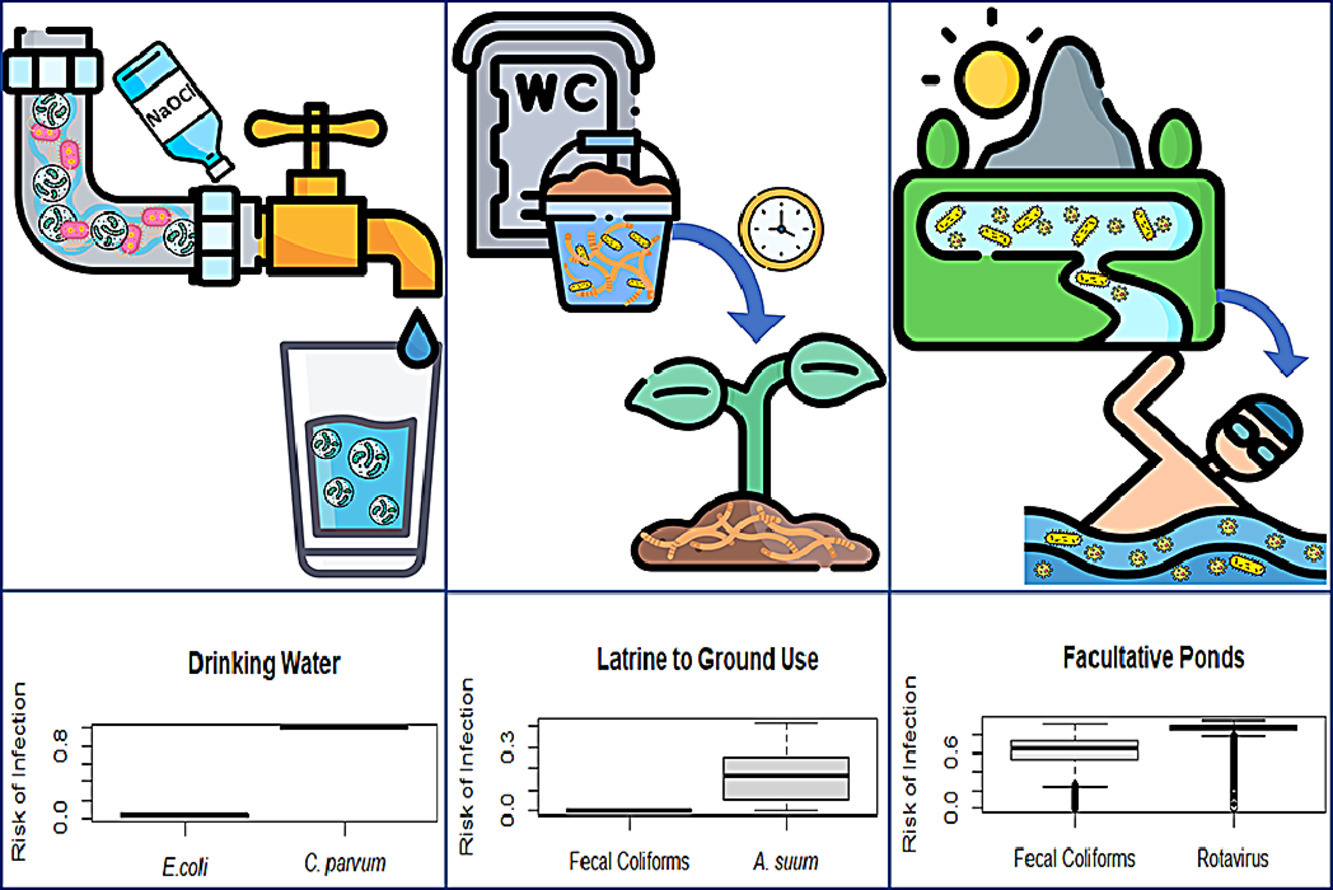
Elsevier, Water Research, Volume 189, 1 February 2021
Water and wastewater utilities, water and sanitation hygiene (WASH) practitioners, and regulating bodies, particularly in developing nations, rely heavily on indicator microorganisms, as opposed to pathogens, for much of their regulatory decisions. This commentary illustrates the importance of considering pathogens and not relying only on indicator organisms when making decisions regarding water and sanitation, especially with respect to meeting the current targets of the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6.
Elsevier, Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America, Volume 47, February 2021
It is estimated that 32.5 million US adults have clinical osteoarthritis (OA), with the most common sites being knee and hip. OA is associated with substantial individual and societal costs. Race/ethnicity, socioeconomic status (SES), and geographic variations in the prevalence of knee and hip OA are well established around the world. In addition, clinical outcomes associated with hip and knee OA differ according to race/ethnicity, SES, and geography. This variation is likely multifactorial and may also reflect country-specific differences in health care systems.
Elsevier, Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America, Volume 41, February 2021
Pollens are a major cause of seasonal allergic diseases. Weather may alter the production of pollens. Increased atmospheric temperatures lead to earlier pollination of many plants and longer duration of pollination, resulting in extended pollen seasons, with early spring or late winter. Longer pollen seasons increase duration of exposure, resulting in more sensitization, and higher pollen concentrations may lead to more severe symptoms. Climate changes in contact to pollens may affect both allergic sensitization and symptom prevalence with severity.
Elsevier, Pediatric Clinics of North America, Volume 68, February 2021
The burden imposed by pollution falls more on those living in low-income and middle-income countries, affecting children more than adults. Most air pollution results from incomplete combustion and contains a mixture of particulate matter and gases. Air pollution exposure has negative impacts on respiratory health. This article concentrates on air pollution in 2 settings, the child's home and the ambient environment. There is an inextricable 2-way link between air pollution and climate change, and the effects of climate change on childhood respiratory health also are discussed.
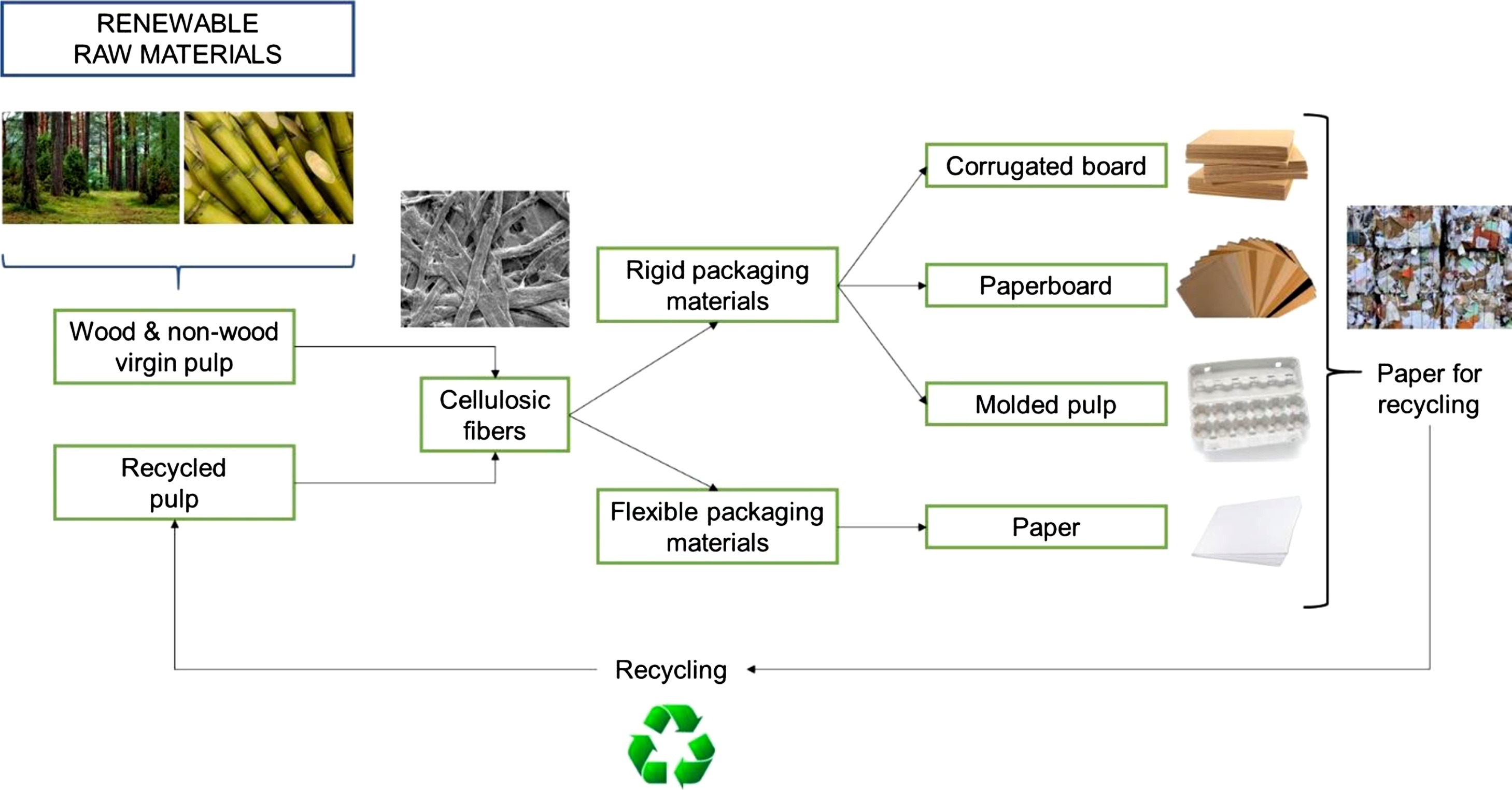
Elsevier, Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 254, 15 February 2021
This short communication describes the climate change impacts of using cellulose, and more precisely cellulosic fiber-based materials, in food packaging, representing current and emerging industrial state of the art technology, without specific reference to current scientific advances. First, the different types of cellulosic fiber-based packaging materials, which can be used to replace fossil-based packaging materials, are presented for flexible and rigid applications. The focus is on technological solutions with packaging properties that enable the protection of commonly sold food products.
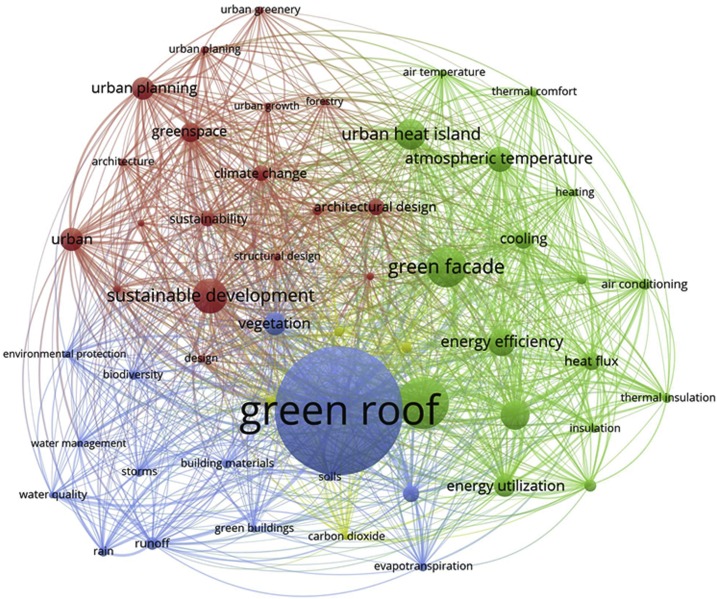
Elsevier, Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 65, February 2021
This study presents a critical review analysis of greenery systems research through a bibliometric approach. The purpose of this study is to provide a holistic overview by (i) the development of the field; (ii) the research trends and the main issues; and (iii) the main gaps still observed in the literature. Therefore, this paper provides the past, the present and the potential future of this scientific topic and serves as an orientation and guide for researchers who aim for a better understanding of the main progress and gaps.
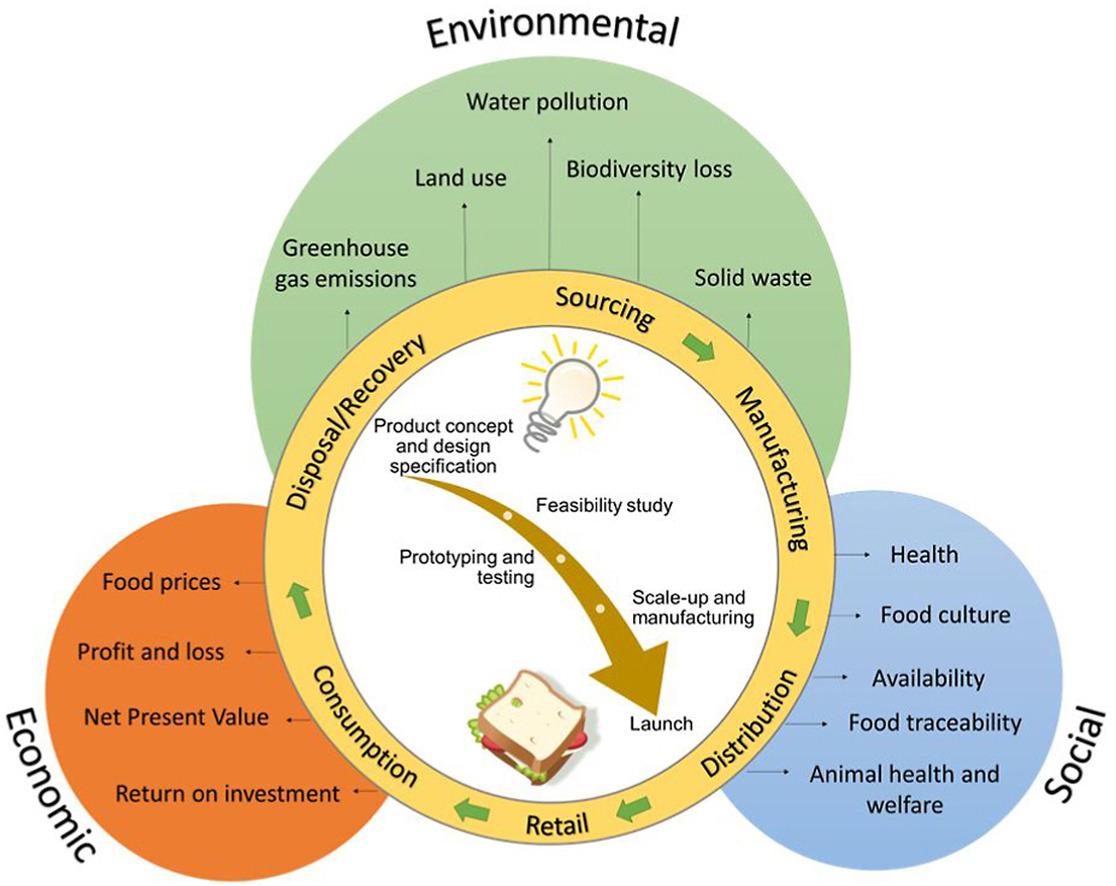
Elsevier, Trends in Food Science and Technology, Volume 108, February 2021
The food industry is responsible for significant impacts on the environment, such as climate change, water depletion and land use. Although these environmental impacts, along with socio-economic ramifications, are generally difficult to monitor and control, there is a significant interest from the food industry to assess the sustainability of their activities and wider supply chains. However, new food products are being continuously designed and manufactured, for instance complex foods made with a number of ingredients such as sandwiches, prepared salads and ready meals.
Elsevier, China Economic Review, Volume 65, February 2021
Mitigating global warming is the responsibility of all countries. Moreso, the role of forests in sequestrating carbon is very crucial. Most environmental organizations are active in protecting the environment according to their objectives. This paper investigates the relationship between institutional freedom and forest carbon sinks by using a panel threshold model with 139 countries to verify the U-shaped relationship between forest carbon sinks and economic development. The U-shaped curve between forest carbon sinks and economic development is the same as the environmental Kuznets curve.
Elsevier, One Earth, Volume 4, 19 February 2021
Despite the importance of tropical forest conservation in achieving global sustainability goals and the key role of forest-risk commodity trade in driving deforestation, consumer country policy options for reducing imported deforestation have received limited scholarly attention. Drawing on gray literature and a European Commission public consultation, we identify 86 policy options for the European Union to address deforestation.
Elsevier, Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation, Volume 171, February 2021
In the recent past, biomedical domain has become popular due to digital image processing of accurate and efficient diagnosis of clinical patients using Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD). Appropriate and punctual disease identification and treatment arrangement directs to enhance superiority of life and improved life hope in Alzheimer Disease (AD) patients. The cutting-edge approaches that believe multimodal analysis have been shown to be efficient and accurate are improved compared with manual analysis.