Elsevier,
The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health, Volume 3, December 2019
An Article in support of SDGs 2 and 3, analysing the burden of child and maternal malnutrition across all states in India, highlighting the progress so far and efforts needed to achieve the national 2022 and global 2030 targets.
Elsevier,
Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry, Volume 1, December 2019
This paper summarizes the literature findings regarding the most widely and consistently accepted diagnostic biomarkers of the f Alzheimer's disease (AD) continuum according to ATN classification. It examined their diagnostic accuracy for AD in comparison with healthy elderly controls and those with other types of dementias and also discussed their limitations and the reasons behind their limited use in routine clinical settings. Moreover, new research avenues in developing biomarkers were also presented.
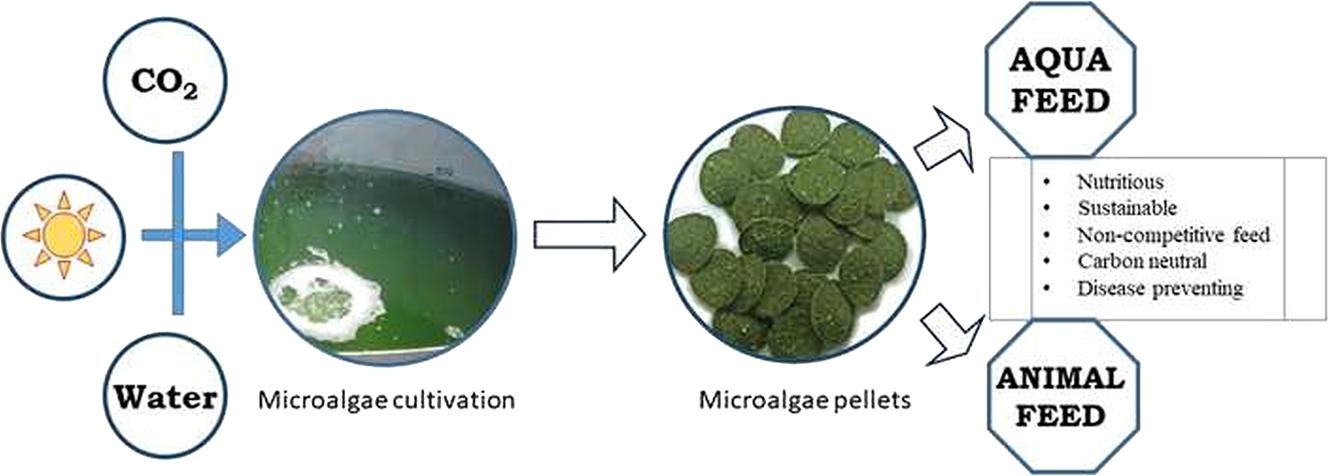
Elsevier, Journal of Functional Foods, Volume 62, November 2019
Aquaculture and animal rearing for meat has increased exceedingly to meet the demands of ever-increasing population. Utilizing small fishes and agricultural products for feed production will lead to over exploitation of the resources and competition with food respectively. Microalgae can be next alternate source for animal and aquatic feed production in an environmentally sustainable and economically advantageous manner.
Elsevier, One Earth, Volume 1, 22 November 2019
Approximately 70% of the aquatic-based production of animals is fed aquaculture, whereby animals are provided with high-protein aquafeeds. Currently, aquafeeds are reliant on fish meal and fish oil sourced from wild-captured forage fish. However, increasing use of forage fish is unsustainable and, because an additional 37.4 million tons of aquafeeds will be required by 2025, alternative protein sources are needed.
Elsevier, One Earth, Volume 1, 22 November 2019
Over US$60 trillion is predicted to be spent on new infrastructure globally by 2040. Is it possible to meet UN Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 9 (develop infrastructure networks) without sacrificing goals 14 and 15 (ending biodiversity loss)? We explore the potential role of “no net loss” (NNL) policies in reconciling these SDGs.
Elsevier, Journal of Neuroscience Methods, Volume 327, 1 November 2019
Background: Compared to previous neuropsychological investigations with standard paper-pen tests limited to test complex spatial learning and memory processes, 3-D virtual immersive technology might offer new tools for research purposes and for diagnosis in patients suffering from mild cognitive impairment or dementia. Comparison with existing methods: Current software proposes a customizable VR environment combined with an analyser module based on regions of interest and some parameters of analysis or pre-calibrated VR mazes with raw data.
Elsevier, Neuron, Volume 104, 20 November 2019
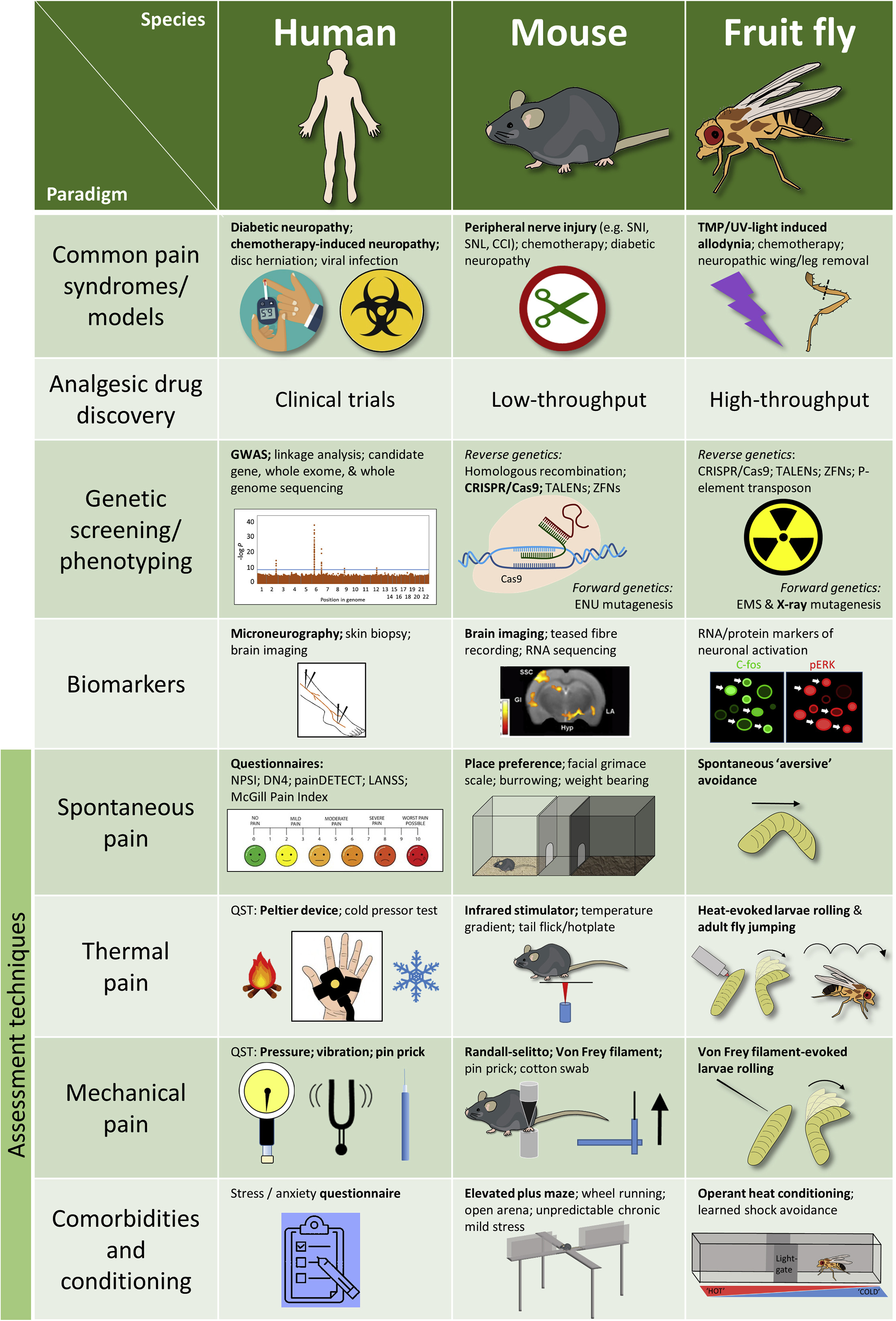
Neuropathic pain (NeuP) arises due to injury of the somatosensory nervous system and is both common and disabling, rendering an urgent need for non-addictive, effective new therapies. Given the high evolutionary conservation of pain, investigative approaches from Drosophila mutagenesis to human Mendelian genetics have aided our understanding of the maladaptive plasticity underlying NeuP. Successes include the identification of ion channel variants causing hyper-excitability and the importance of neuro-immune signaling.
Elsevier, The Lancet, Volume 394, 9 - 15 November 2019
Background: Women across the world are mistreated during childbirth. We aimed to develop and implement evidence-informed, validated tools to measure mistreatment during childbirth, and report results from a cross-sectional study in four low-income and middle-income countries. Methods: We prospectively recruited women aged at least 15 years in twelve health facilities (three per country) in Ghana, Guinea, Myanmar, and Nigeria between Sept 19, 2016, and Jan 18, 2018. Continuous observations of labour and childbirth were done from admission up to 2 h post partum.
Elsevier, Soil and Tillage Research, Volume 194, November 2019
Historically, tillage has been essential for seedbed preparation and weed control, but it has also accelerated soil degradation through erosion and loss of soil organic matter (SOM). Our objective was to quantify the changes in soil physical properties and earthworm abundance under six tillage treatments on an Endocalcic Chernozem (Loamic) soil (2016 and 2017).
Elsevier, Soil and Tillage Research, Volume 194, November 2019
As a response to the worldwide challenge raised by soil degradation, Conservation Agriculture (CA) was proposed to help restoring the three main soil functions, i.e. carbon transformation, nutrient cycling and structure maintenance. However, there is still a lack of integrative studies that assess the overall impact of CA on soil health. To fill the gap, Biofunctool®, a set of in-field indicators, was developed to monitor changes in soil biological functioning.