World Water Day is an annual United Nations Observance focusing on the importance of freshwater and raising awareness of the 2.2 billion people living without access to safe water. On March 22, 2021, World Water Day will be celebrated in an online event. The World Water Day celebrates water and raises awareness of the global water crisis, and a core focus of the observance is to support the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6: water and sanitation for all by 2030.
Originally started in 1993, this year’s theme of World Water Day 2021 is valuing water. The value of water is about much more than its price – water has enormous and complex value for our households, food, culture, health, education, economics and the integrity of our natural environment. If we overlook any of these values, we risk mismanaging this finite, irreplaceable resource. SDG 6 is to ensure water and sanitation for all. Without a comprehensive understanding of water’s true, multidimensional value, we will be unable to safeguard this critical resource for the benefit of everyone. Today, water is under extreme threat from a growing population, increasing demands of agriculture and industry, and the worsening impacts of climate change.
To raise awareness of the value of water, Elsevier presents a curated list of free access journal articles and book chapters. At Elsevier, we are advancing #SDG6 research and ensuring that #Everydrop counts.
Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 61, October 2020
Urbanisation is increasing in many countries, leading to the establishment of 33 megacities, representing huge water demand which is increasingly difficult to supply, exemplified by the recently avoided Day Zero event in Cape Town (2018) and the ongoing water crisis in Chennai, India. The ongoing growth of megacities could lead to the potential for further Day Zero events in countries ill-equipped to deal with such a situation. This study analyses the water supply and demand situations in 12 megacities hosting 194 million people.
Sustainable Water Engineering, 2020, Pages 99-120
Biopolymer Membranes and Films, 2020, pages 359-382
Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Water and Wastewater Advanced Treatment Processes, 2020, Pages 139-176
Sustainable Water Resource Development Using Coastal Reservoirs, 2020, Pages 33-59
International Encyclopedia of Public Health (Second Edition), 2017, Pages 350-360
International Encyclopedia of Public Health (Second Edition), 2017, Pages 148-158
Water Conservation and Wastewater Treatment in BRICS Nations, 2020, Pages 187-211
Drought Early Warning and Forecasting, 2020, Pages 1-21
Global Groundwater, 2021, Pages 145-162
Global Groundwater, 2021, Pages 347-357
Advances in Chemical Pollution, Environmental Management and Protection, Volume 6, 2020, Pages 1-31
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, Volume 230, September 2020
Background: Access to safe sanitation and the elimination of open defecation are pre-conditions for improved child health and nutrition and wider achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). While Indonesia has a solid policy framework, the country ranks third globally in terms of numbers of people practicing open defecation. Objectives: Our aim was to assess the effectiveness of a five-year strategy to reduce open defecation through accelerating implementation of the national sanitation program across districts receiving variable levels of external support.
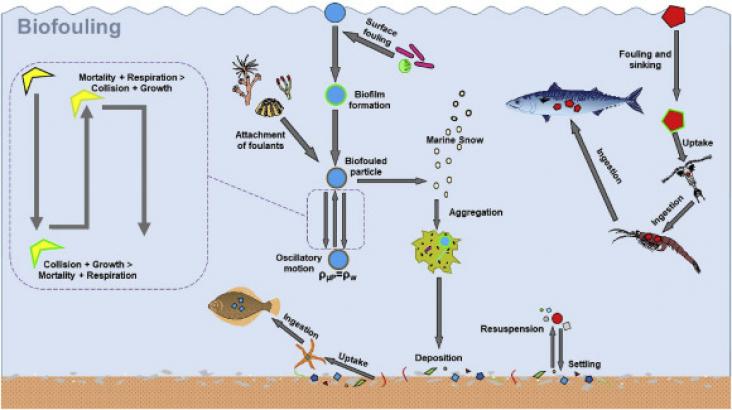
Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Volume 2, September 2020
As the global production of plastics continues to accelerate, the ubiquitous presence of microplastics (μPs) has emerged as a significant marine problem. To comprehend fully the potential impacts and ecological harm caused by μPs it is vital that there is an understanding of their potential sources and sinks; the processes affecting their distribution; and their uptake and exchange in ecosystems.
Encyclopedia of Health Economics, 2014, Pages 477-482
GIS and Geostatistical Techniques for Groundwater Science, 2019, Pages 57-78