Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, Volume 148, June 2021
Children with disabilities in Ontario, Canada have their right to equal access to education protected by the 1990 Ontario Human Rights Code and the 1990 Education Act. These legislated rights require the delivery of stigma- and barrier-free education services to children with disabilities. However, the extent to which compliance is achieved by school boards and individual schools is questionable and warrants attention as a matter of both scholarship and public policy.
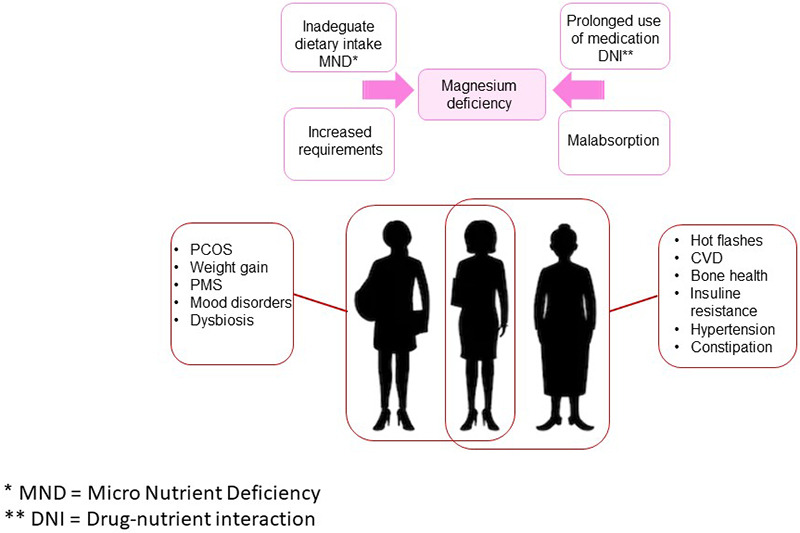
eClinicalMedicine, Volume 36, June 2021
EClinicalMedicine, Volume 36, June 2021
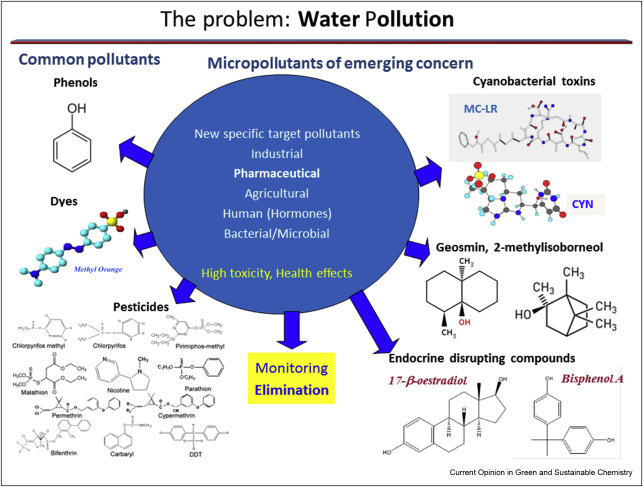
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 29, June 2021