Agricultural Systems, Volume 177, January 2020
Elucidating relationships between the soil food web, soil processes, and agroecosystem function is a critical step toward a more sustainable agriculture. Soil and crop management practices can alter these relationships, and their effects can persist even after imposing new management practices. In 2005, the Cornell Organic Grain Cropping Systems Experiment was established in central New York. Four cropping systems that varied in fertilizer inputs, tillage practices, and weed control were compared: High Fertility, Low Fertility, Enhanced Weed Management, Reduced Tillage.
Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 52, January 2020
The UN 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the 169 targets have been considered in multidisciplinary approaches worldwide. Whereas, several environmental, economic and social development concerns have been covered by the UN 2030 Agenda. The aim of this research is to investigate the complexity of the interactions between building materials and the SDGs, in an attempt to establish a knowledge-based decision support system for policy-makers, designers and construction stakeholders regarding the implementation of 2030 agenda.
Resources, Conservation and Recycling, Volume 152, January 2020
Circular economy strategies seek to reduce the total resources extracted from the environment and reduce the wastes that human activities generate in pursuit of human wellbeing. Circular Economy concepts are well suited to the building and construction sector in cities. For example, refurbishing and adaptively reusing underutilized or abandoned buildings can revitalize neighborhoods whilst achieving environmental benefits. Cultural heritage buildings hold a unique niche in the urban landscape.
Environment International, Volume 134, January 2020
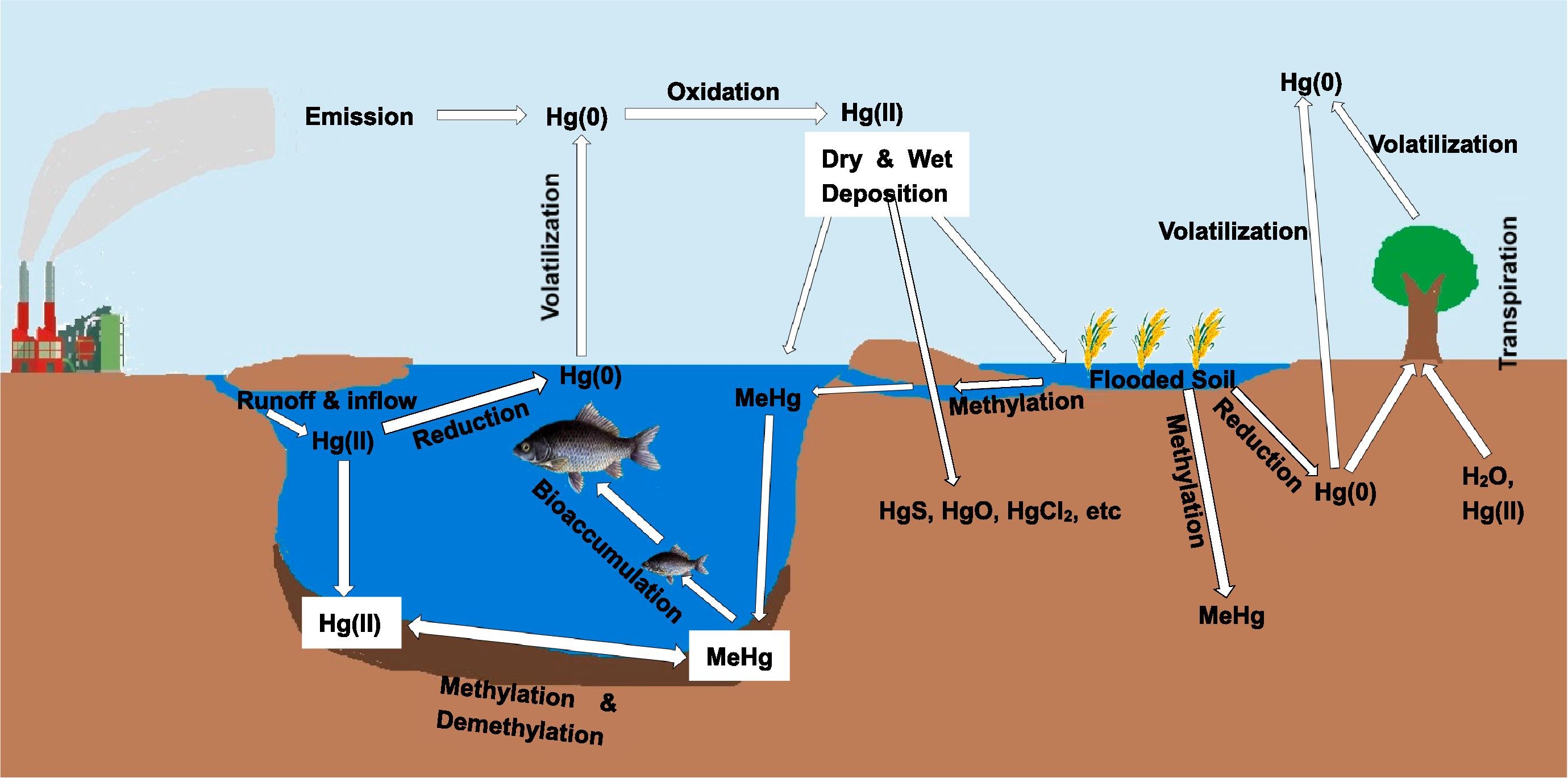
Mercury contamination in soil, water and air is associated with potential toxicity to humans and ecosystems. Industrial activities such as coal combustion have led to increased mercury (Hg) concentrations in different environmental media. This review critically evaluates recent developments in technological approaches for the remediation of Hg contaminated soil, water and air, with a focus on emerging materials and innovative technologies.
Agricultural Water Management, Volume 227, 20 January 2020
Soil and water salinity and associated problems are a major challenge for global food production. Strategies to cope with salinity include a better understanding of the impacts of temporal and spatial dynamics of salinity on soil water balances vis-à-vis evapotranspiration (ET) and devising optimal irrigation schedules and efficient methods. Both steady state and transient models are now available for predicting salinity effects on reduction of crop growth and means for its optimization.
Trends in Food Science and Technology, Volume 95, January 2020
Background: Fruits and vegetables are an excellent source of nutrients, with numerous health benefits. Most consumers are not meeting the daily recommended intake of fruits and vegetables. Yet, a significant amount of fruits and vegetables that is produced is wasted. There are opportunities to recover the wasted fruits and vegetables for manufacturing value-added products to improve the sustainability of healthy diets and reduce the environmental footprint.