Elsevier, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, Volume 182, February 2019
It has been estimated that European customers visit community pharmacies to access essential primary healthcare around 46 million times every day. Studies of dispensing error rates in community pharmacies have reported error rates of between 0.08% and 3.3% per item dispensed. While severe cases of dispensing inaccuracies often garner a high level of media coverage, less significant errors are also causing inefficiencies in primary healthcare delivery.
Elsevier, Trends in Ecology and Evolution, Volume 34, February 2019
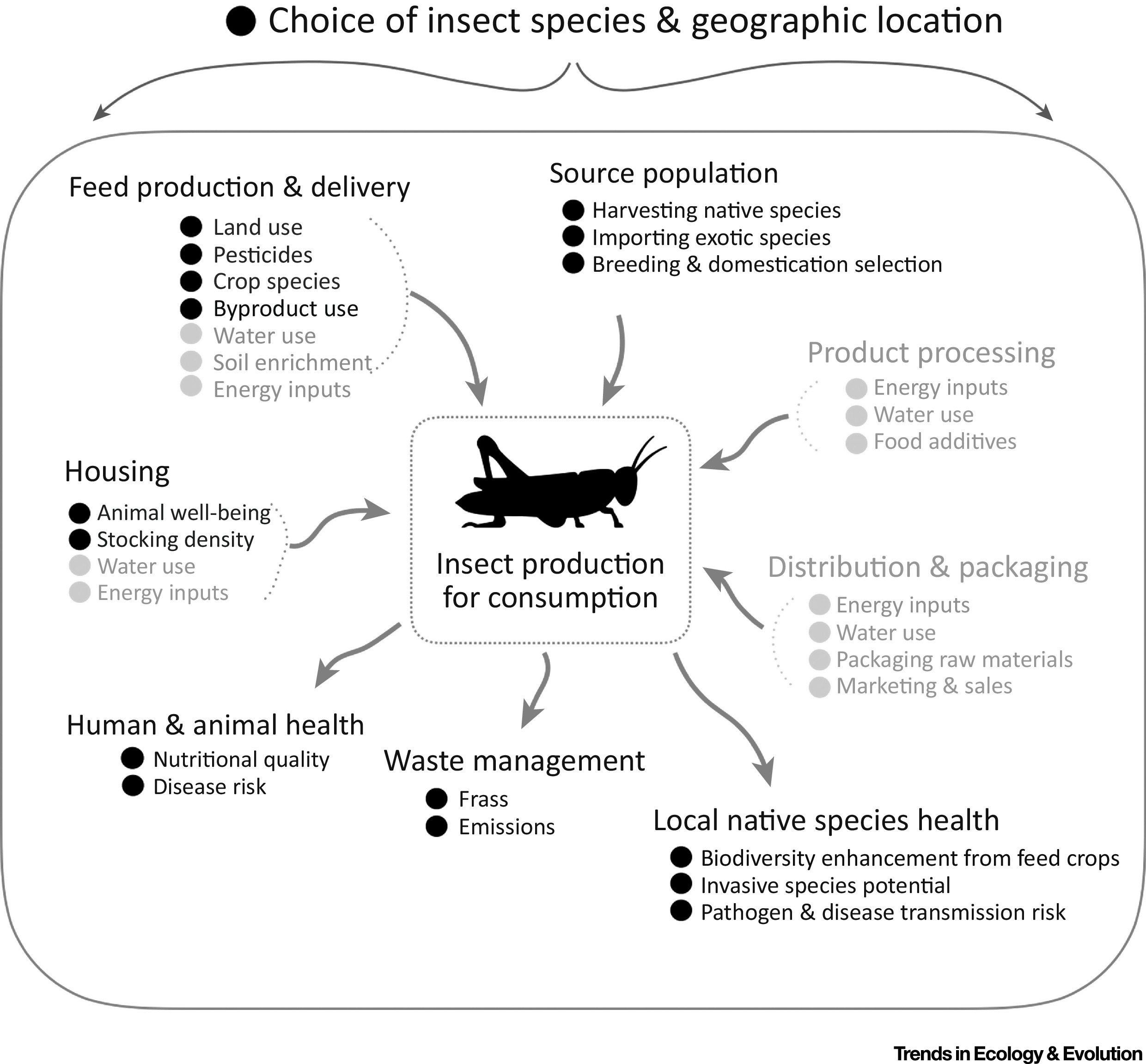
The emerging insects-as-food industry is increasingly promoted as a sustainable alternative to other animal protein production systems. However, the exact nature of its environmental benefits are uncertain because of the overwhelming lack of knowledge concerning almost every aspect of production: from suitable species, their housing and feed requirements, and potential for accidental release.
Elsevier, Trends in Ecology and Evolution, Volume 34, February 2019
There is worldwide concern about the environmental costs of conventional intensification of agriculture. Growing evidence suggests that ecological intensification of mainstream farming can safeguard food production, with accompanying environmental benefits; however, the approach is rarely adopted by farmers. Our review of the evidence for replacing external inputs with ecosystem services shows that scientists tend to focus on processes (e.g., pollination) rather than outcomes (e.g., profits), and express benefits at spatio-temporal scales that are not always relevant to farmers.
Elsevier, The Lancet, Volume 393, 9 - 15 February 2019
Women's representation in science and medicine has slowly increased over the past few decades. However, this rise in numbers of women, or gender diversity, has not been matched by a rise in gender inclusion. Despite increasing representation, women still encounter bias and discrimination when compared with men in these fields across a variety of outcomes, including treatment at school and work, hiring, compensation, evaluation, and promotion.