Habitat International, Volume 117, November 2021
Ethiopia has experienced rapid urbanization over the past three decades. Several cities expanded rapidly and many satellite towns sprung up around the major cities. The high rate of urbanization and urban growth resulted in high demand for urban land, mainly for industrial, commercial, and residential purposes. In order to meet the demand, an enormous amount of land has been made available for urban use, mainly through land conversion. However, we know very little about how efficiently cities use urban land.
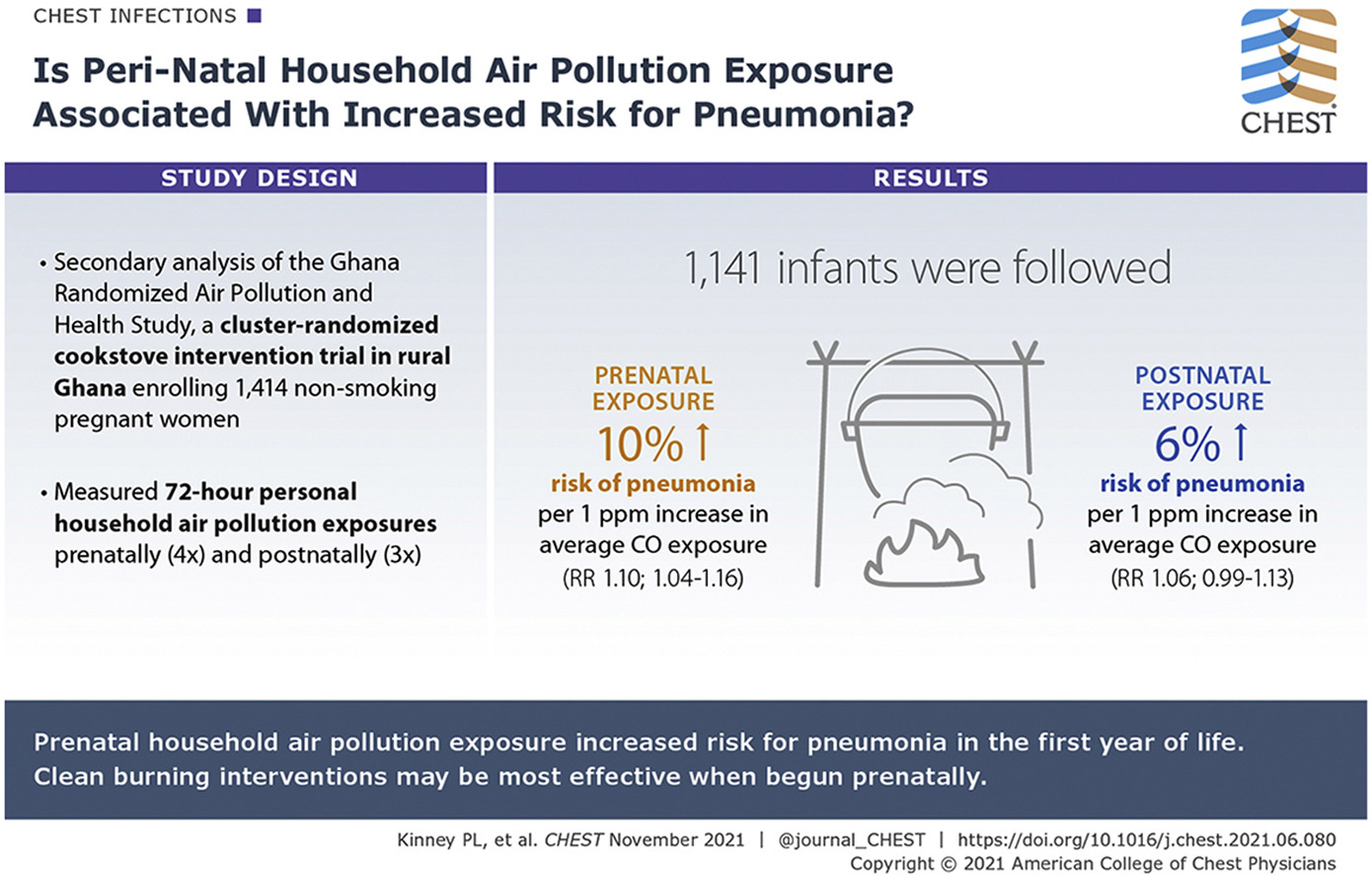
Chest, Volume 160, November 2021
Background: Nearly 40% of the world's population is exposed daily to household air pollution. The relative impact of prenatal and postnatal household air pollution exposure on early childhood pneumonia, a leading cause of mortality, is unknown. Research Question: Are prenatal or postnatal household air pollution, or both, associated with pneumonia risk in the first year of life? Study Design and Methods: The Ghana Randomized Air Pollution and Health Study enrolled 1,414 nonsmoking, pregnant women before 24 weeks’ gestation with prospective follow-up to the child's age of 1 year.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, November 2021
Background: The announcement of China's 2060 carbon neutrality goal has drawn the world's attention to the specific technology pathway needed to achieve this pledge. We aimed to evaluate the health co-benefits of carbon neutrality under different technology pathways, which could help China to achieve the carbon neutrality goal, air quality goal, and Healthy China goal in a synergetic manner that includes health in the decision-making process.
Energy Strategy Reviews, Volume 38, November 2021
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 12, 1 November 2021