5th April 2016
Critical Perspectives on Accounting, Volume 35, March 01, 2016
There is a paucity of research on sexuality within accounting studies in general, and next to nothing on lesbian, gay, bisexual and trans* (LGBT) sexualities in particular. One major problem associated with this neglect is that the heteronormative bias within the accounting studies goes unchallenged, reproducing a heterosexual/homosexual binary that posits heterosexuality as a normative standard by which other sexualities are judged and found wanting.
Energy and Buildings, Volume 116, 15 March 2016
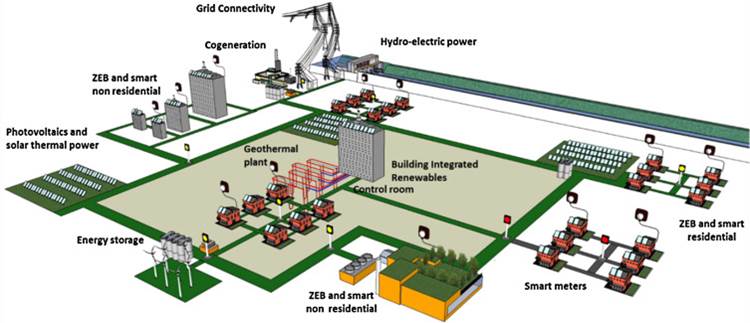
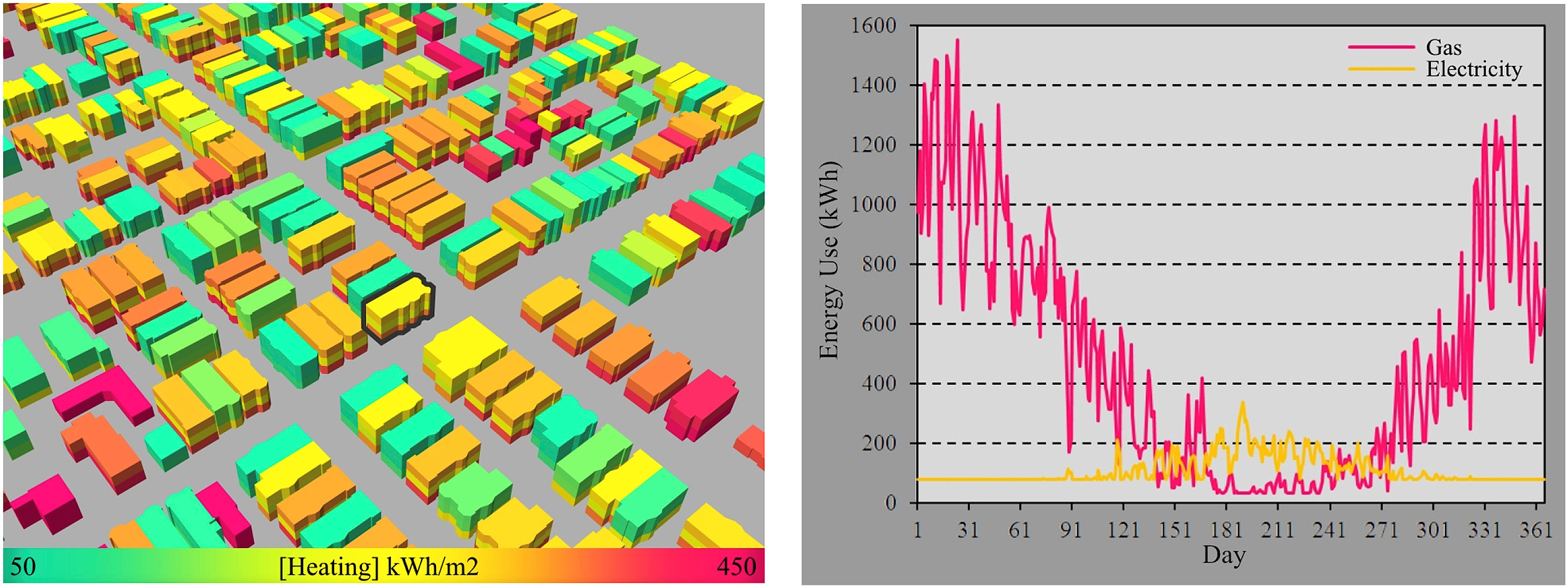
The smart grids are modern electric power grid infrastructure for enhanced efficiency and reliability through automated control, high-power converters, modern communications infrastructure, sensing and metering technologies, and modern energy management techniques based on the optimization of demand, energy and network availability. The role of buildings in this framework is very crucial. This paper addresses critical issues on smart grid technologies and the integration of buildings in this new power grid framework.