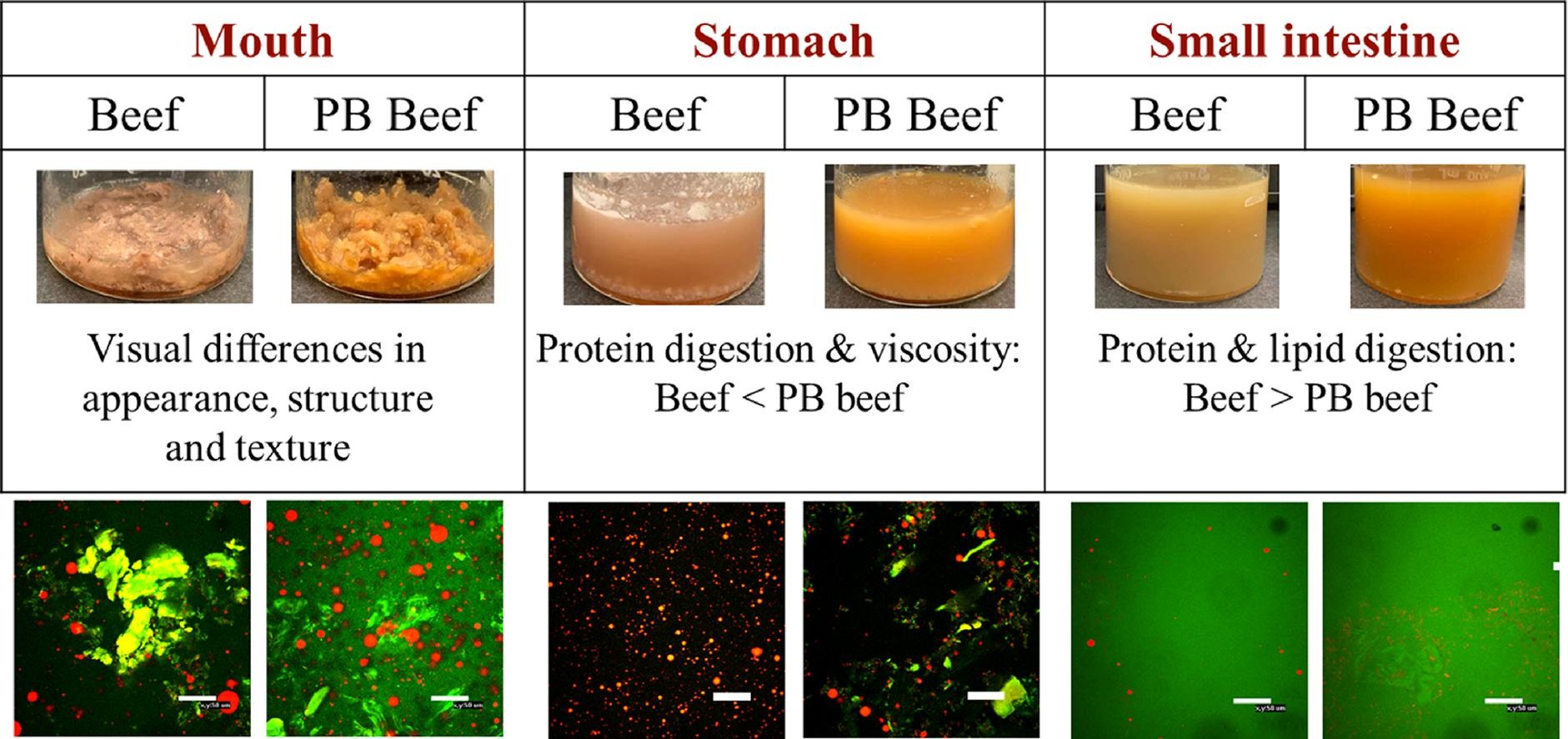
Food Chemistry, Volume 364, 1 December 2021
Plant-based meat analogs are likely to have different gastrointestinal fates than real meat products due to differences in their compositions and structures. Here, we compared the gastrointestinal fate of ground beef and ground beef analogs using the INFOGEST in vitro digestion model, focusing on differences in microstructure, physicochemical properties, lipid digestion, and protein digestion in different regions of the model gut.
Food Quality and Preference, Volume 94, December 2021
Using data from Eurobarometer 83.4, this study combines the two branches of research that address climate-related and biodiversity-related opinions and actions of individuals in the EU. The literature shows that the differences between climate-related and biodiversity-related policies correspond, at an individual level, to a person's basic attitudes towards environmental protection and towards nature protection, respectively.
Future Foods, Volume 4, December 2021
The global market for plant-based foods intended as alternatives to cheese products is increasing and will reach almost $4 billion by 2024. In this study, an evaluation of the composition, structure and physicochemical properties of four commercial plant-based block-style products was conducted, with results compared with those for Cheddar and processed cheeses. The plant-based products had considerably lower protein contents (0.11–3.00%) compared to the Cheddar and processed cheeses (25.04 and 18.50%, respectively).
Future Foods, Volume 4, December 2021
Substitution of beef with alternative proteins is one practical trend taken by industry and consumers to reduce the negative impact of convenience products on the environment. Numerous products based on plant, insect and fungi proteins compete to replace beef burgers in an environmentally friendly and healthy way. At the same time, there is a lack of studies which assess different options from environmental impact perspective but also with consideration of production scales, recipes, nutritional values, and sensory properties.
Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, Volume 28, December 2021
By the year 2019, the number of people without access to electricity was 770 million, most of which lived in rural areas. The currently models for rural electrification are often limited in their electrical analysis, or focus on a idealistic optimal solution whilst ignoring the real hierarchical topology of power systems. This work proposes a rural electrification strategy that makes use of Geographic Information System (GIS), graph theory and terrain analysis to create the best electric network topology.
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, Volume 42, December 2021
The mounting research on consumer behavior and climate change is gradually improving our understanding of effective ways to mobilize consumers to mitigate climate change. The relationship between consumer behavior and climate change is complex and most consumers are not capable of determining which behavior changes are worth doing. Research has come a long way identifying the most impactful behavior changes, but more research is needed to refine and situate these insights.
The Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 4, December 2021