Elsevier, Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 8, December 2017
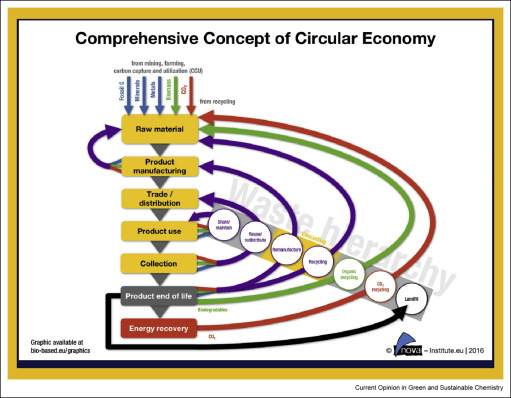
Waste is an extremely valuable resource that we have been accumulating over a long period. Interesting and viable organic “waste-to-resource” opportunities include plastics and food supply chain wastes. Their use as chemical feedstocks will fit well with a circular economy model. Plastics is a major waste opportunity: worldwide we only recycle a few % of the plastic we use, yet plastic manufacturing consumes some 10% of all the oil we consume, and much of it causes serious environmental damage through negligent release.
Elsevier, Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 8, December 2017
The replacement of the fossil resources historically employed for chemicals’ production is of major scientific interest the last decades, as a result of the environmental issues arisen and the price versatility of petroleum. Biotechnological routes present promising alternatives for the production of various platform chemicals such as succinic, lactic and muconic acids among others. The utilisation of agricultural and agro-industrial waste and by-product streams would not only reduce the overall production cost but also it would assist towards the direction of the bio-economy era.
Elsevier, Global Food Security, Volume 15, December 2017
This paper shows that despite progress in reducing extreme poverty, little progress has been made in reducing the number of people living on between $1.25 and $2 a day and it provides updated estimates of rural and urban poverty for regions throughout the developing world. It then shows the dramatic growth in recent decades in government expenditures on social protection, defined broadly. Next it shows that social assistance coverage is lowest and amounts transferred the smallest in parts of the world where poverty is most widespread.
Elsevier, Tourism Management, Volume 63, December 2017
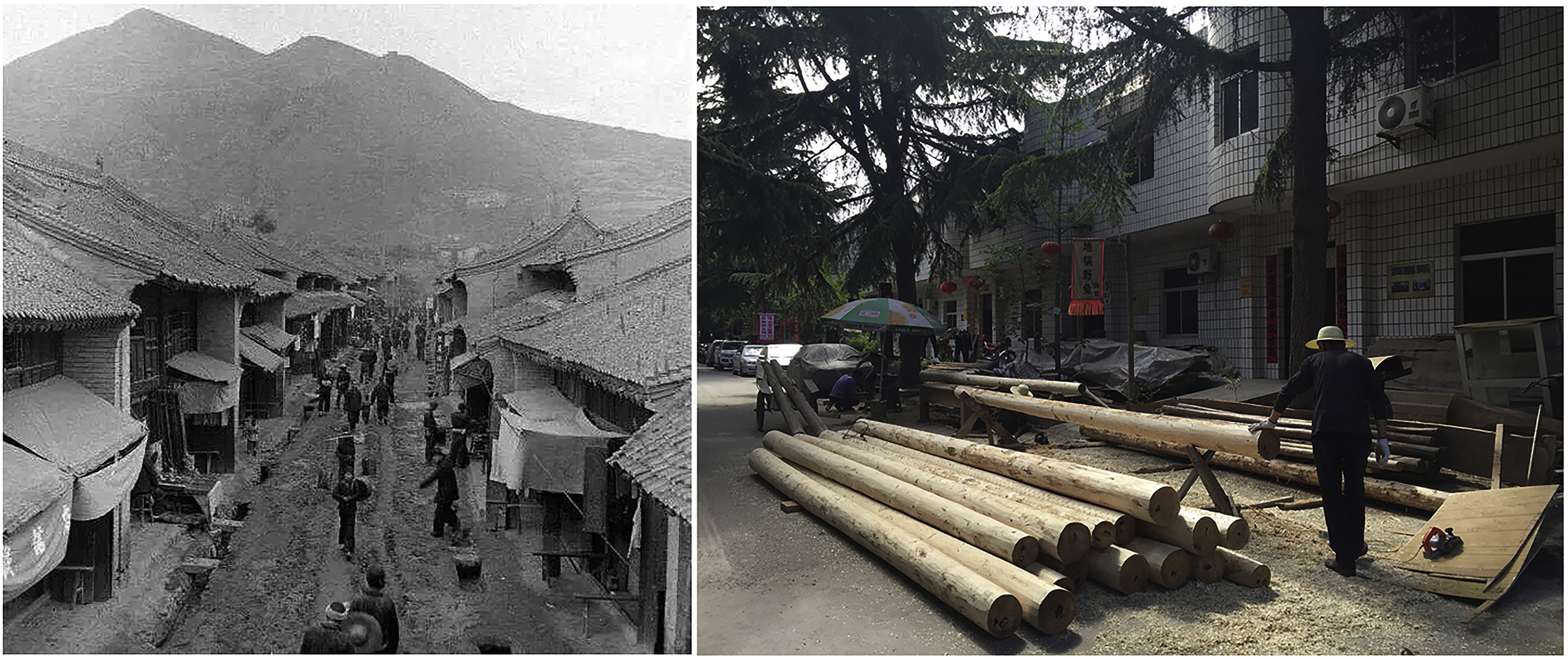
Increasing attention has been given to historically and culturally significant traditional villages in China in the past five years. Two key themes have been protection and usage. Rural tourism has been recognized as a key approach to rural development and poverty alleviation. Through a systematic knowledge review, this paper proposes an integrative and sustainable Rural Tourism-based Traditional Village Revitalization model to better understand the relationship between rural tourism and village revitalization.
Elsevier, The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 2, December 2017
The WHO global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis, created in May, 2016, aims to achieve a 90% reduction in new cases of chronic hepatitis B and C and a 65% reduction in mortality due to hepatitis B and C by 2030. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa, and despite the introduction of universal hepatitis B vaccination and effective antiviral therapy, the estimated overall seroprevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen remains high at 6·1% (95% uncertainty interval 4·6–8·5).
Elsevier, The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 2, December 2017
In 2016, WHO adopted a strategy for the elimination of viral hepatitis by 2030. Africa, and more specifically, sub-Saharan Africa, carries a substantial portion of the global burden of viral hepatitis, especially chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections. The task that lies ahead for sub-Saharan Africa to achieve elimination is substantial, but not insurmountable. Major developments in the management of hepatitis C have put elimination within reach, but several difficulties will need to be navigated on the path to elimination.
Elsevier, The Lancet HIV, Volume 4, December 2017
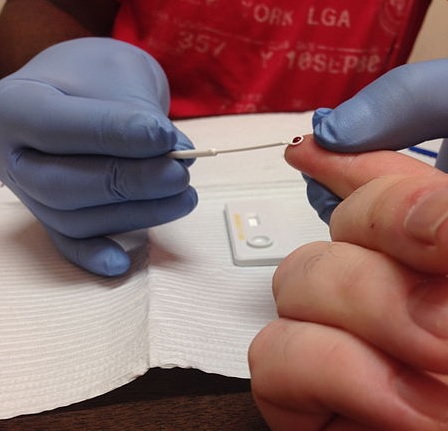
Background Multistage, stepwise HIV testing and treatment procedures can result in lost opportunities to provide timely antiretroviral therapy (ART). Incomplete engagement of patients along the care cascade translates into high preventable mortality. We aimed to identify whether a structural intervention to streamline testing and linkage to HIV health care would improve testing completeness, ART initiation, and viral suppression and reduce mortality. Methods We did a cluster-randomised, controlled trial in 12 hospitals in Guangxi, China.
Elsevier,
International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, Volume 328, 1 December 2017
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health as well as Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by discussing the impact of chromatin structure on viral integration, transcriptional regulation and latency, and the host factors that influence HIV-1 replication by regulating chromatin organization.