Elsevier,
Social Sciences & Humanities Open, Volume 3, Issue 1, 2021, 100112
This article explores how men living in Istanbul talk about the sociality of house and care work – vacuuming the house, cooking, doing the laundry – in their everyday lives. The authors believe that the existing trends in so-called ordinary days will enable us to understand the extent to which gender roles are either challenged or re-constructed at home.
This study investigates how the sources of carbon emissions affect life expectancy. The study sample includes 68 developing and emerging economies for the period 1990-2017. Disaggregated analysis is performed on: (1) emissions sources; (2) income groups. A negative nexus between life expectancy and CO2 emissions exists for emerging ones. However, CO2 emissions seem to improve the life expectancy for developing countries.
Elsevier, LWT, Volume 156, 15 February 2022
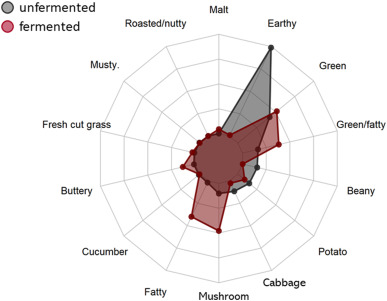
Plant proteins can serve as inexpensive and environmentally friendly meat-replacements. However, poor taste characteristics and relatively low nutritional value prevent their full acceptance as meat substitutes. Fermentation of food has been historically used to improve the quality of foods. In this work we describe the improvement in digestibility, nutritional value, physical properties, and organoleptic characteristics, of a pea and rice protein concentrate blend through fermentation with shiitake mushroom mycelium.
Elsevier, The Lancet Global Health, Volume 10, February 2022
Background: China has the highest prevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection worldwide. Universal HBV screening might enable China to reach the WHO 2030 target of 90% diagnostics, 80% treatment, and 65% HBV-related death reduction, and eventually elimination of viral hepatitis. We evaluated the cost-effectiveness of implementing universal HBV screening in China and identified optimal screening strategies.