Joule, Volume 4, 14 October 2020
Wolf-Peter Schill is Deputy Head of the Energy, Transportation, Environment Department at the German Institute for Economic Research (DIW Berlin), where he leads the research area Transformation of the Energy Economy. He engages in open-source power sector modeling, which he applies to economic analyses of renewable energy integration, energy storage, and sector coupling. He holds a diploma in environmental engineering and a doctoral degree in economics from Technische Universität Berlin.
Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 61, October 2020
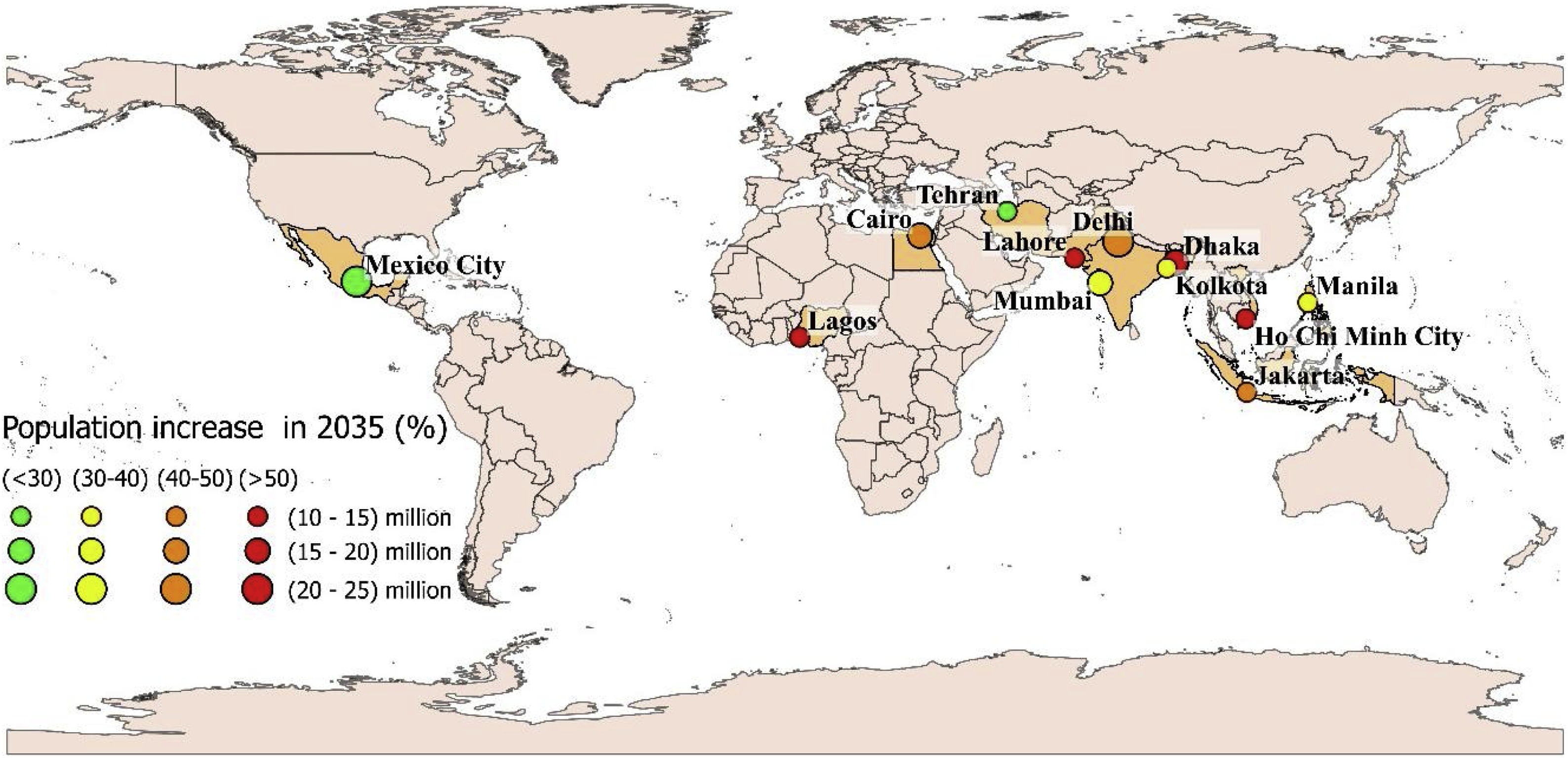
Urbanisation is increasing in many countries, leading to the establishment of 33 megacities, representing huge water demand which is increasingly difficult to supply, exemplified by the recently avoided Day Zero event in Cape Town (2018) and the ongoing water crisis in Chennai, India. The ongoing growth of megacities could lead to the potential for further Day Zero events in countries ill-equipped to deal with such a situation. This study analyses the water supply and demand situations in 12 megacities hosting 194 million people.
Current Opinion in Environmental Science and Health, Volume 17, October 2020
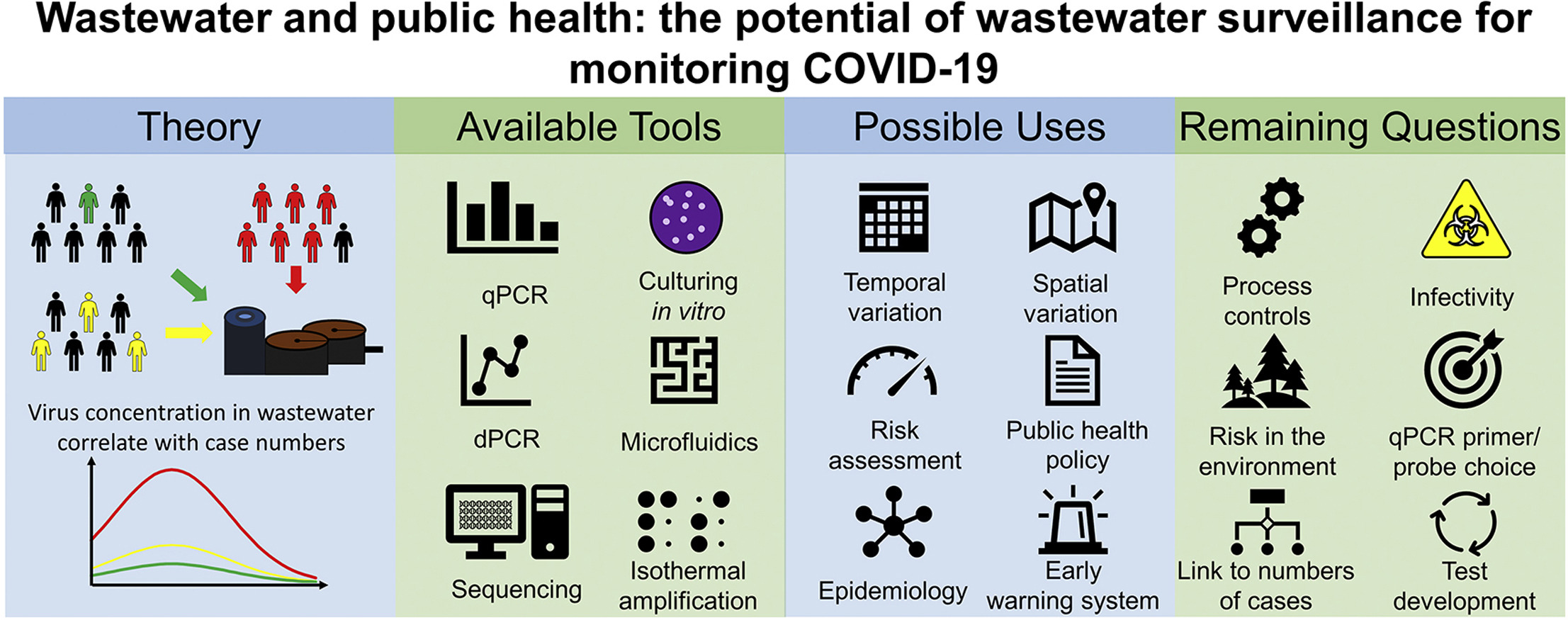
Pathogenic viruses represent one of the greatest threats to human well-being. As evidenced by the COVID-19 global pandemic, however, halting the spread of highly contagious diseases is notoriously difficult. Successful control strategies therefore have to rely on effective surveillance. Here, we describe how monitoring wastewater from urban areas can be used to detect the arrival and subsequent decline of pathogens, such as SARS-CoV-2.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 4, October 2020
Background: Approximately 2·8 billion people are exposed to household air pollution from cooking with polluting fuels. Few monitoring studies have systematically measured health-damaging air pollutant (ie, fine particulate matter [PM2·5] and black carbon) concentrations from a wide range of cooking fuels across diverse populations. This multinational study aimed to assess the magnitude of kitchen concentrations and personal exposures to PM2·5 and black carbon in rural communities with a wide range of cooking environments.