Elsevier, iScience, Volume 23, 20 November 2020
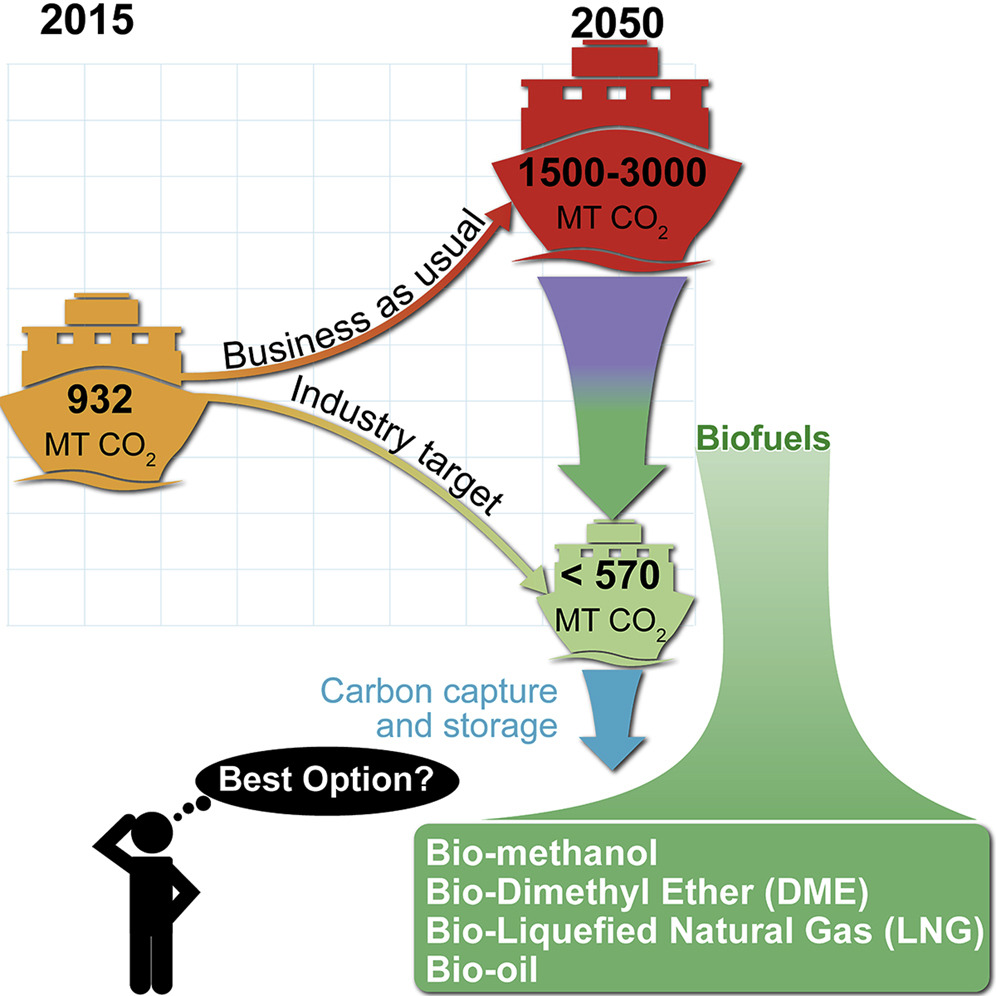
The greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the marine sector were around 2.6% of world GHG emissions in 2015 and are expected to increase 50%–250% to 2050 under a “business as usual” scenario, making the decarbonization of this fossil fuel-intensive sector an urgent priority. Biofuels, which come in various forms, are one of the most promising options to replace existing marine fuels for accomplishing this in the short to medium term.
Elsevier, Psychosomatics, Volume 61, 1 November 2020
Background: Coronovirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) first broke out in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, in 2019, and now it spreads in more than 100 countries around the world. On January 30th, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a public health emergency of international concern. It was classified as a pandemic by the WHO on March 11, 2020. With the increase in the number of cases reported by various countries every day, the COVID-19 pandemic has attracted more and more attention around the world.
Elsevier, Current Research in Food Science, Volume 3, November 2020
The principal motivations for the worldwide trend towards reducing meat consumption are health, the environment and animal welfare. The present study investigated the willingness of omnivores to introduce mixed (beef-vegetable protein) and 100% vegetable protein products into their diet. The participants (n = 251) were young adult omnivores who consumed meat at least once a week. The stimuli were images of six different products representing two beef burgers, two mixed-protein burgers (50% beef and 50% seitan or soy) and two 100% vegetable protein burgers (seitan and soy).
Elsevier, The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, November 2020
Background: Stay-at-home orders (lockdowns) have been deployed globally to control COVID-19 transmission, and might impair economic conditions and mental health, and exacerbate risk of food insecurity and intimate partner violence. The effect of lockdowns in low-income and middle-income countries must be understood to ensure safe deployment of these interventions in less affluent settings. We aimed to determine the immediate impact of COVID-19 lockdown orders on women and their families in rural Bangladesh.
Elsevier, The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, November 2020
Background: Stay-at-home orders (lockdowns) have been deployed globally to control COVID-19 transmission, and might impair economic conditions and mental health, and exacerbate risk of food insecurity and intimate partner violence. The effect of lockdowns in low-income and middle-income countries must be understood to ensure safe deployment of these interventions in less affluent settings. We aimed to determine the immediate impact of COVID-19 lockdown orders on women and their families in rural Bangladesh.
Elsevier, Catena, Volume 194, November 2020
With ongoing global climate change and human activities, increasing desertification plays a predominant role in increasing soil nutrient losses. Soil nitrogen (N) is the essential limiting nutrient supporting plant growth and evaluating soil nutrient content, especially in desert ecosystems. N microbial processes will ultimately restore and maintain the balance in the soil N cycle, but the damage caused by desertification to soil N functional microorganisms associated with N supply, transformation, and loss is poorly understood.
Elsevier, Women's Studies International Forum, Volume 83, 1 November 2020
This paper provides a critical feminist analysis of seven policies relating to gender equality in the agriculture sector of Ethiopia. A review of 22 major documents that outline legislation and policy frame the feminist analysis. Despite the strong commitment of the Government of Ethiopia (GoE) toward gender equality and gender mainstreaming, many of the policies analyzed do not integrate gender equality as a priority for the growth and development of the country and do not adequately mainstream gender.
Elsevier, Advances in Radiation Oncology, Volume 5, 1 November 2020
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to assess the current status of gender disparities in academic radiation oncology departments in the United States and the associated factors. Methods and Materials: The data were collected from publicly available resources, including websites of individual radiation oncology programs, the Fellowship and Residency Electronic Interactive Database, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, and the Association of American Medical Colleges.