Elsevier, Biomass and Bioenergy, Volume 125, June 2019
Rising demand for renewable resources has increased silage maize (Zea mays L.)production characterized by intensive soil management, high fertilizer and pesticide inputs as well as simplified crop rotations. Advantages of renewable biomass production may thus be cancelled out by adverse environmental effects. Perennial crops, like cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.), are said to benefit arthropods. Substituting silage maize could hence increase biodiversity and foster ecosystem services.
Elsevier, World Development, Volume 118, June 2019
Understanding the politics of education reform is crucial to assess the challenges facing the SDG of quality education. This article surveys the small academic literature on the politics of reform as well as a wide range of empirical research on reform experiences across the world, with an emphasis on recent reforms in Latin America. We focus on teacher policy reforms, which play a central role in raising learning in primary and secondary schools, but pose three special challenges.
Elsevier, World Development, Volume 118, June 2019
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development is ambitious and inclusive, but how well are these global aspirations likely to result in implementable policy change for water and sanitation? This article assesses governance challenges at the local level associated with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6, which pledges to ensure sustainable water and sanitation for all. The majority of developing countries manage services at the subnational level, making the quality of local governance the key ingredient for improvements in the sector.
Elsevier, Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, Volume 97, June 2019
The aggregation of fibrils of hyperphosphorylated and C-terminally truncated microtubule-associated tau protein characterizes 80% of all dementia disorders, the most common neurodegenerative disorders. These so-called tauopathies are hitherto not curable and their diagnosis, especially at early disease stages, has traditionally proven difficult. A keystone in the diagnosis of tauopathies was the development of methods to assess levels of tau protein in vivo in cerebrospinal fluid, which has significantly improved our knowledge about these conditions.
Elsevier, The Lancet Public Health, Volume 4, June 2019
Background: Evidence for online interventions to help women experiencing intimate partner violence is scarce. We assessed whether an online interactive healthy relationship tool and safety decision aid (I-DECIDE) would increase women's self-efficacy and improve depressive symptoms compared with an intimate partner violence information website. Methods: In this two-group pragmatic randomised controlled trial, we enrolled women who had screened positive for any form of intimate partner violence or fear of a partner in the 6 months before recruitment.
Elsevier, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, Volume 278, 1 June 2019
Anthropogenic climate change is altering the functioning of terrestrial ecosystems. Agricultural systems are particularly vulnerable to climate change as they are frequently disturbed by intensified management practices. This also threatens belowground organisms that are responsible for providing crucial ecosystem functions and services, such as nutrient cycling and plant disease suppression. Amongst these organisms, earthworms are of particular importance as they can modulate the effects of climate change on soil organisms by modifying the biotic and abiotic soil conditions.
Elsevier, Science of the Total Environment, Volume 669, 15 June 2019
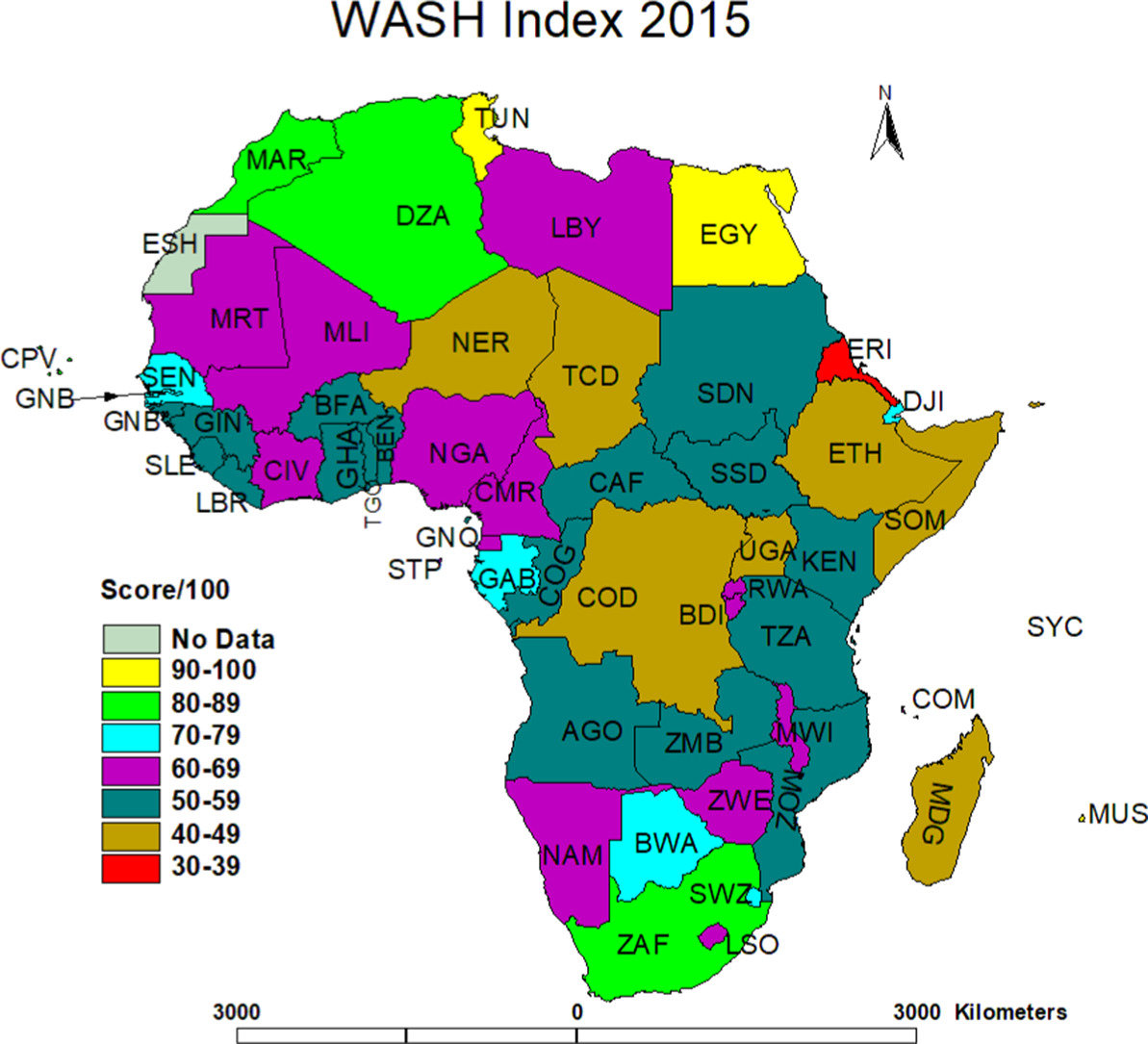
Water–Sanitation–Hygiene (WASH) remains vital for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, yet many countries have not localised the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 6, which focuses on ensuring the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. Even in leading African economies such as South Africa, many communities still use the bucket system for sanitation.
Elsevier, Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Volume 190, June 2019
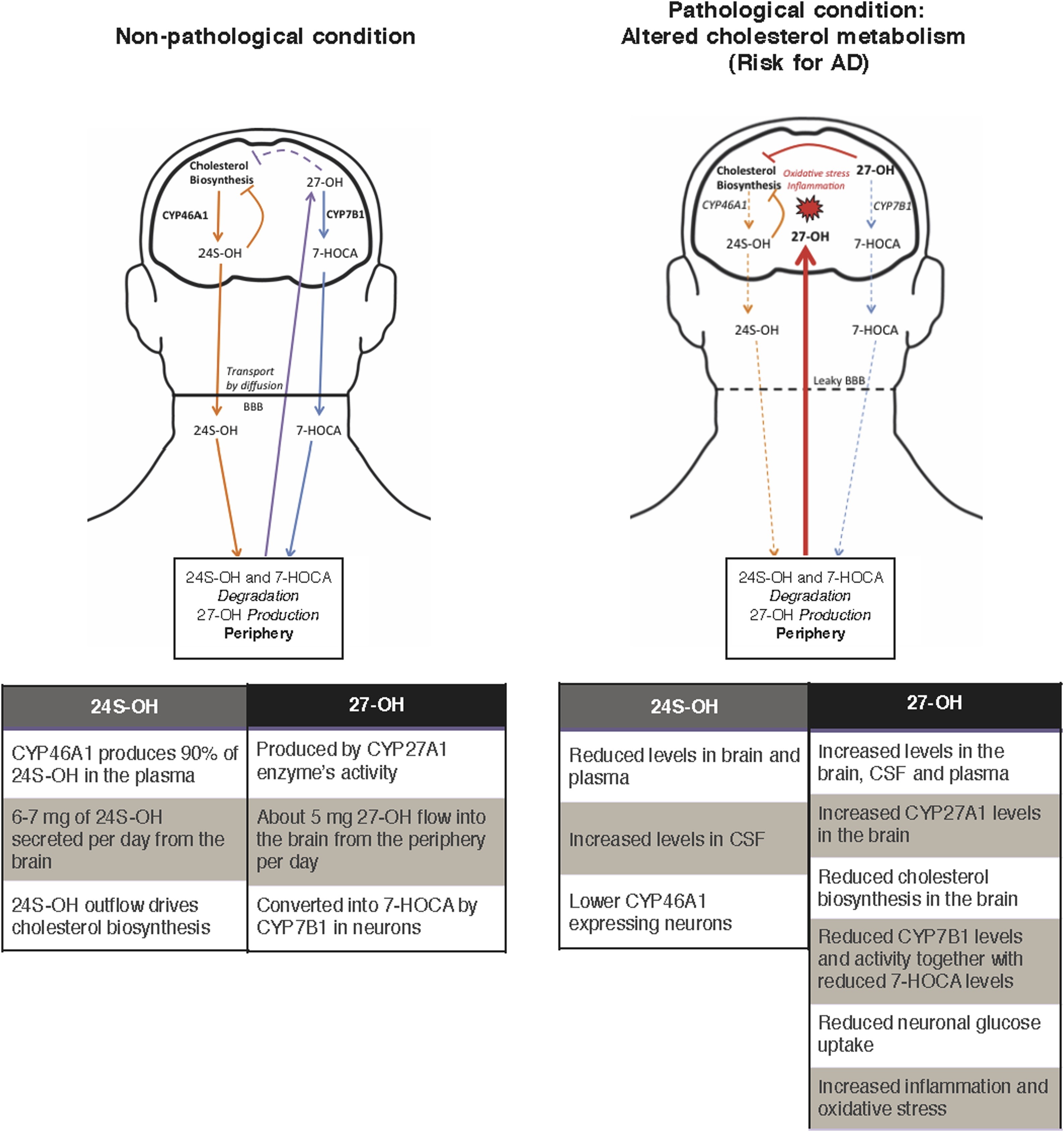
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and it is characterized by the deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. However, the complete pathogenesis of the disease is still unknown. High level of serum cholesterol has been found to positively correlate with an increased risk of dementia and some studies have reported a decreased prevalence of AD in patients taking cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Elsevier, Cortex, Volume 115, June 2019
Background: Memory for music has attracted much recent interest in Alzheimer's disease but the underlying brain mechanisms have not been defined in patients directly. Here we addressed this issue in an Alzheimer's disease cohort using activation fMRI of two core musical memory systems. Methods: We studied 34 patients with younger onset Alzheimer's disease led either by episodic memory decline (typical Alzheimer's disease)or by visuospatial impairment (posterior cortical atrophy)in relation to 19 age-matched healthy individuals.
Elsevier, iScience, Volume 16, 28 June 2019
Microglia play a key role in innate immunity in Alzheimer disease (AD), but their role as antigen-presenting cells is as yet unclear. Here we found that amyloid β peptide (Aβ)-specific T helper 1 (Aβ-Th1 cells) T cells polarized to secrete interferon-γ and intracerebroventricularly (ICV) injected to the 5XFAD mouse model of AD induced the differentiation of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII)+ microglia with distinct morphology and enhanced plaque clearance capacity than MHCII− microglia.