The theme of this year’s #WorldFoodDay is “Water is life, water is food. Leave no one behind.” In celebration of this theme, we are proud to offer a publicly available special collection including more than 40 carefully curated book chapters and journal articles to shine a spotlight on water as the foundation for life and food. This campaign raises awareness for the importance of managing water wisely as the availability of this precious resource is threatened by rapid population growth, urbanization, economic development, and climate change. Download and share this impactful content today.
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 115, 1 January 2022
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 115, 1 April 2022
Food and Bioproducts Processing, Volume 135, September 2022
Nutrition Science, Marketing Nutrition, Health Claims, and Public Policy, 2023, pp 297-305
Precision Agriculture: Evolution, Insights and Emerging Trends, 2023, pp 85-101
Climate Change and Extreme Events, 2021, pp 83-103
Recent Advancements in Wastewater Management: Implications and Biological Solutions, 2023, pp 109-132
Encyclopedia of Inland Waters, Second Edition, 2022, pp 450-463
Water Resource Modeling and Computational Technologies, 2022, pp 17-35
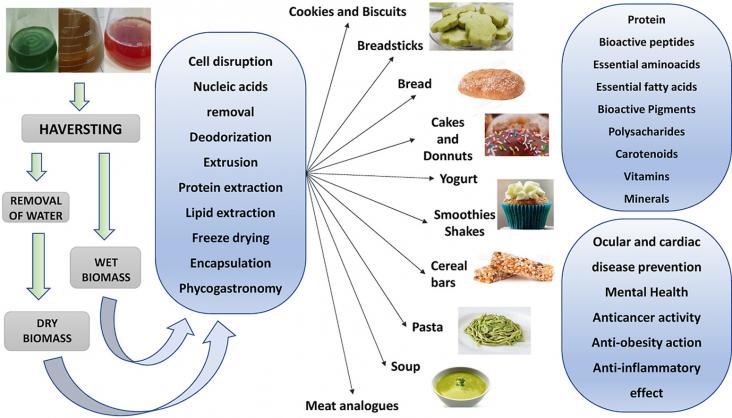
Handbook of Food and Feed from Microalgae: Production, Application, Regulation, and Sustainability, 2023, pp 603-610
Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, Volume 106, 2023, pp 241-274
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 12, 1 November 2021
Trends in Food Science and Technology, Volume 126, August 2022
Journal of Transport Geography, Volume 107, February 2023
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 5, 1 February 2021
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 118, July 2023
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 114, 1 August 2021
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 115, 1 April 2022
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 115, 1 February 2022
Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 5, January 2022
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 116, 1 November 2022
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 113, 1 January 2021
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 114, 1 November 2021
Materials Today Communications, Volume 31, June 2022
Food and Bioproducts Processing, Volume 136, November 2022
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 13, 1 May 2022
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 7, April 2023
Food and Bioproducts Processing, Volume 135, September 2022
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 5, 1 June 2021
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 6, 1 July 2022
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 11, August 2023
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 11, July 2023
Journal of Nutrition, Volume 153, February 2023
One Earth, Volume 6, 20 January 2023