Earth-Science Reviews, Volume 240, May 2023
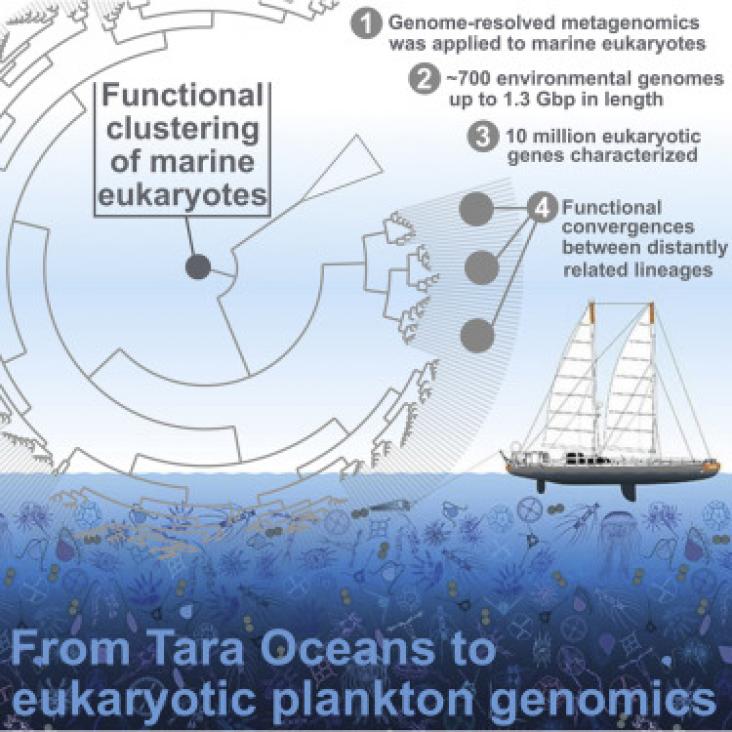
Cell Genomics, Volume 3, 12 April 2023
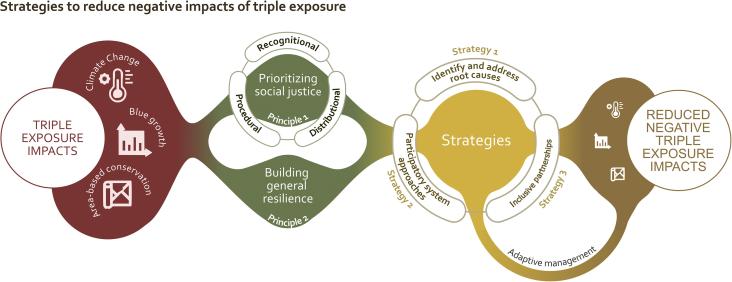
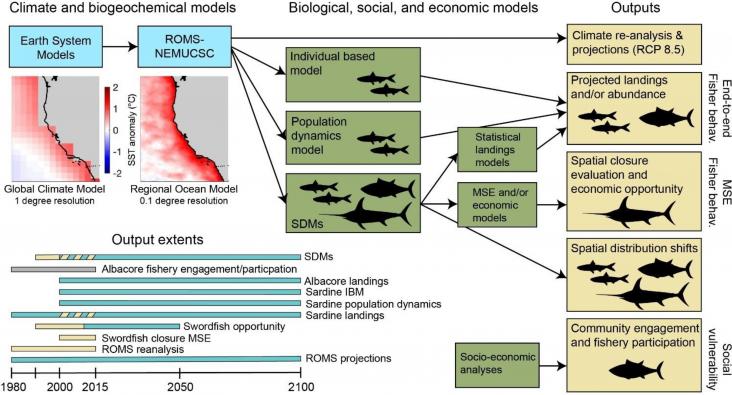
One Earth, Volume 6, 17 February 2023
Environment International, Volume 171, January 2023
Genomics, Volume 114, November 2022
Cell Genomics, Volume 2, 11 May 2022
Aquaculture, Volume 549, 25 February 2022
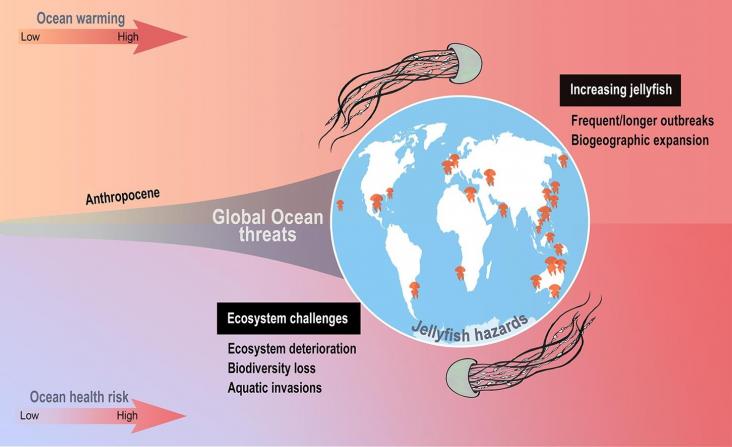
Ocean Acidification and Marine Wildlife, 2021, pp 247-263
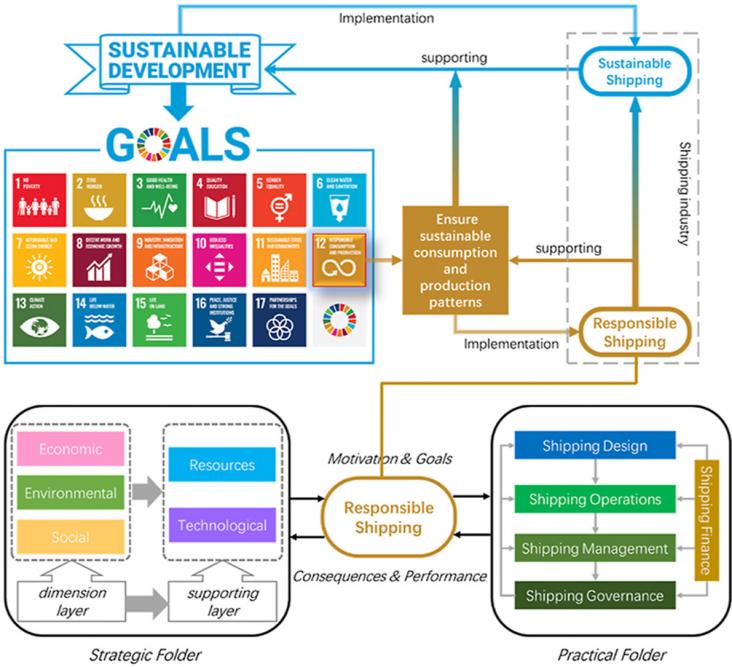
COVID-19 and the Sustainable Development Goals, 2022, pp 285-303
Complementarity of Variable Renewable Energy Sources, 2022, pp 527-558
Field Measurements for Passive Environmental Remote Sensing: Instrumentation, Intensive Campaigns, and Satellite Applications, 2023, pp 79-100
Advances in Virus Research, Volume 114, 2022, pp 67-146
Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals in Metabolic and Non-communicable Diseases, 2022, pp 707-723
Ocean Mixing: Drivers, Mechanisms and Impacts, 2021, pp 5-24
Genomics and the Global Bioeconomy, 2022, pp 125-138
Applied Environmental Metabolomics, 2022, pp 199-209
Ocean Modelling, Volume 183, June 2023
Ocean Modelling, Volume 183, June 2023
Progress in Oceanography, Volume 213, 1 April 2023
Ocean Modelling, Volume 182, April 2023
Progress in Oceanography, Volume 212, March 2023
Progress in Oceanography, Volume 211, February 2023
Ocean Modelling, Volume 181, February 2023
Ocean Modelling, Volume 181, February 2023
Progress in Oceanography, Volume 210, January 2023
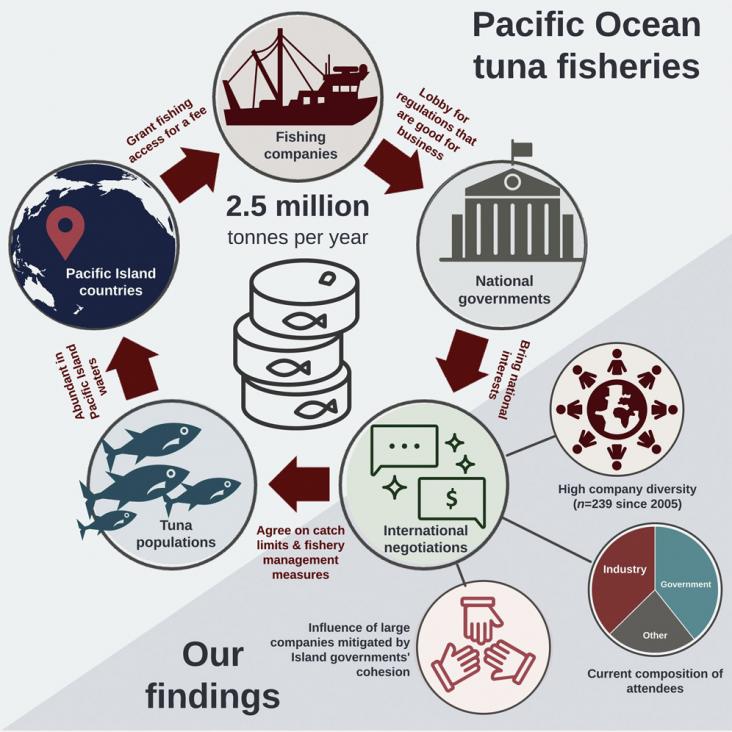
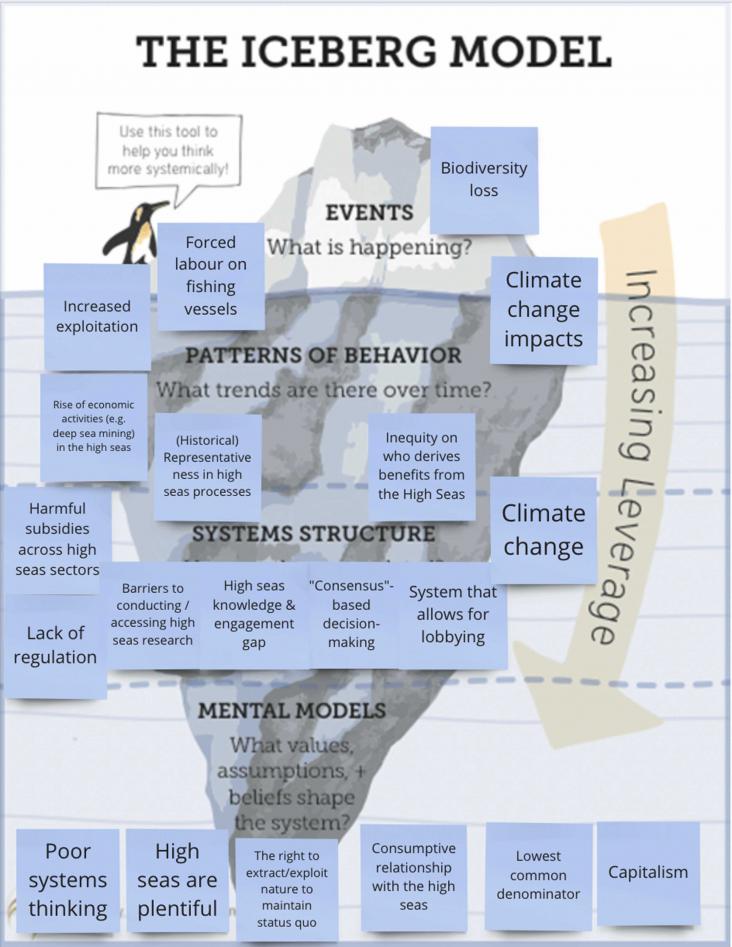
Marine Policy, Volume 153, 2023, 105644, ISSN 0308-597X
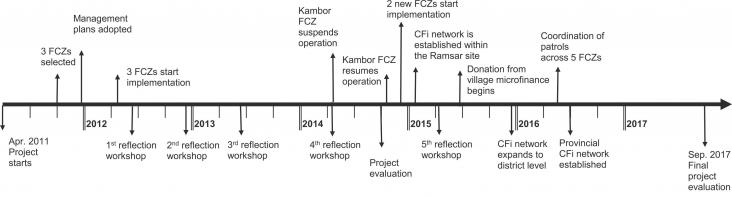
Fisheries Research, Volume 265, 2023, 106744
Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, Volume 565, 2023, 151916