Elsevier, Food Research International, Volume 137, November 2020
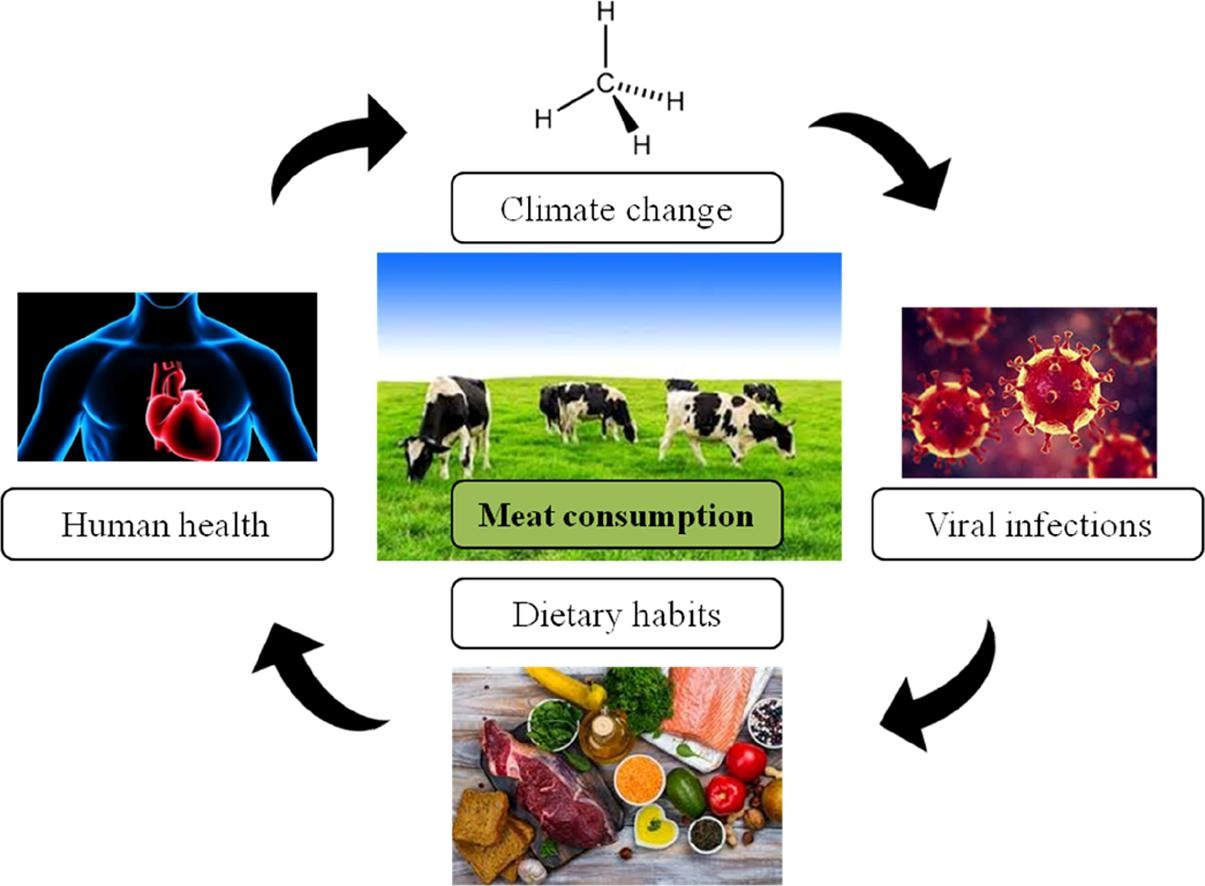
Meat consumption has been increasing since the 1960s, but especially from the 1980s decade to today. Although meat means an important source of nutrients, it is also evident that a great consumption of this source of proteins has also a negative environmental impact. Livestock production does not only have a negative influence on GHG emissions, but also on the water footprint, water pollution, and water scarcity.
Elsevier, Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, Volume 8, November 2020
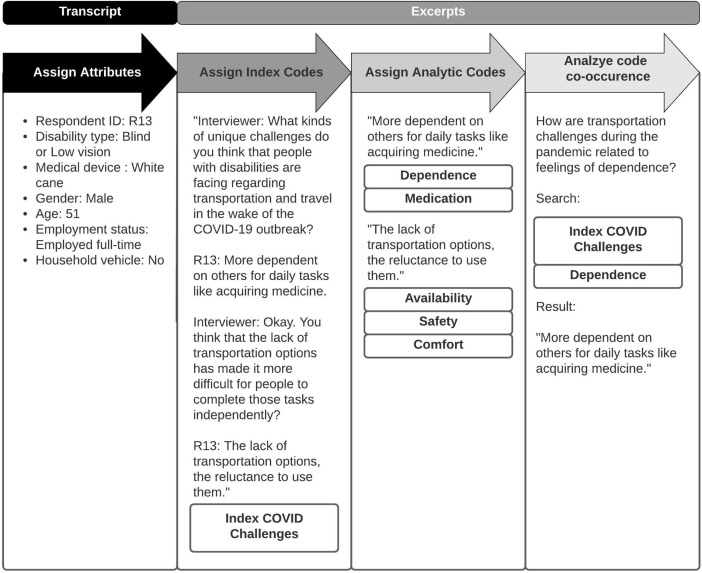
People with disabilities may be particularly vulnerable to the direct health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the wider impacts of the pandemic response. People with disabilities experience numerous barriers to using transportation to access essential goods, like fresh food, and services, like medical care, that are necessary for maintaining health. The pandemic and the pandemic response threaten to exacerbate persistent health disparities and add to transportation barriers that disadvantage people with disabilities.
Elsevier, The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, November 2020
Background: 3 billion people worldwide rely on polluting fuels and technologies for domestic cooking and heating. We estimate the global, regional, and national health burden associated with exposure to household air pollution. Methods: For the systematic review and meta-analysis, we systematically searched four databases for studies published from database inception to April 2, 2020, that evaluated the risk of adverse cardiorespiratory, paediatric, and maternal outcomes from exposure to household air pollution, compared with no exposure.
Elsevier,
Global Food Security,
Volume 27,
2020,
100442,
ISSN 2211-9124,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100442.
This paper provides an overview of children and adolescents’ diet. Food systems need to be redesigned to improve diet quality in children 0-19 years in order to address the multiple burdens of malnutrition. Data systems also need to be strengthened to track data quality among children. This article advances knowledge on SDG 2 and 3.
Elsevier,
12th November 2020
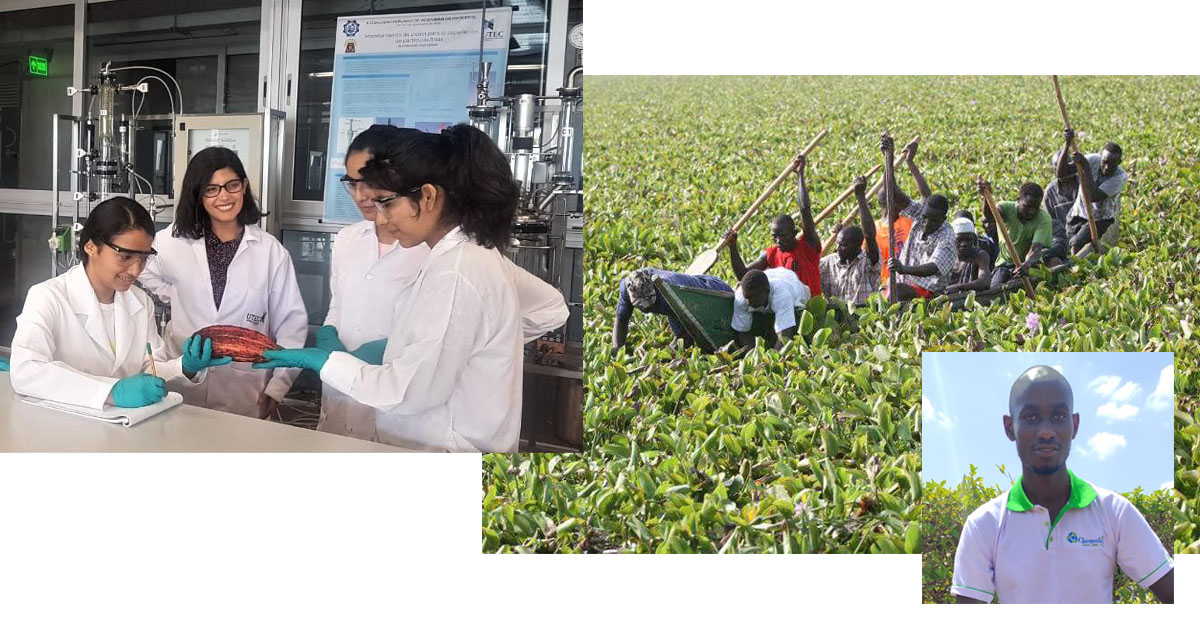
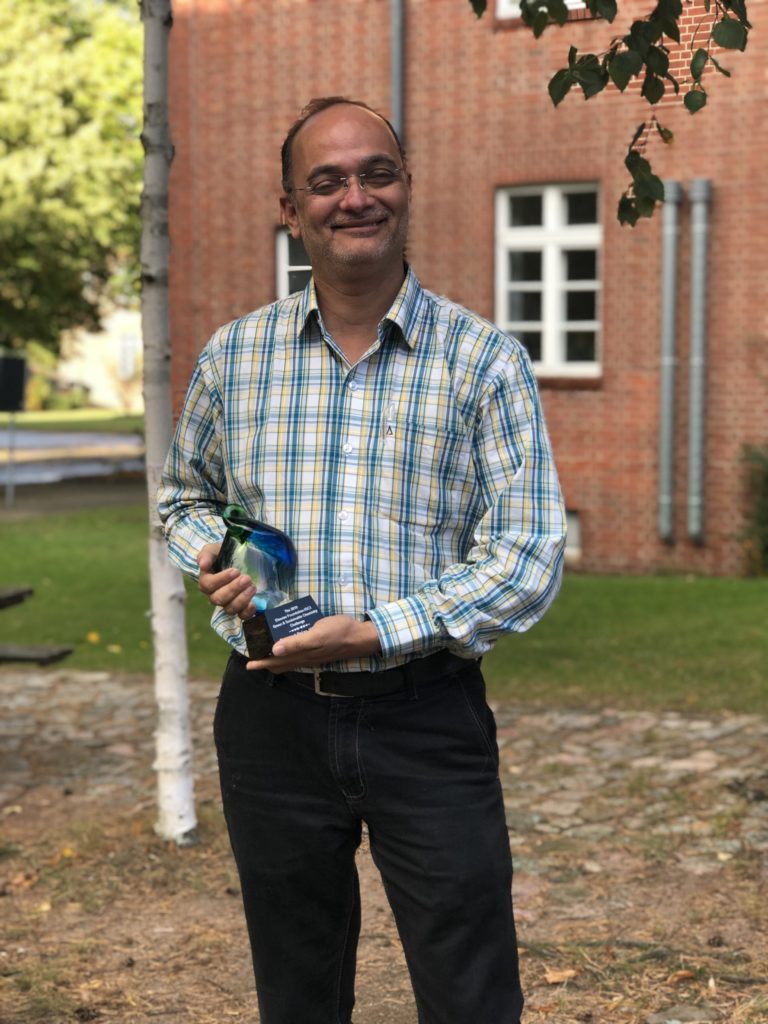
This article highlights the winning proposals of the fifth edition of the Elsevier Foundation Green & Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. The winning proposals were chosen for their innovative green chemistry aspects and their large positive impact on the environment, contributing to SDGs 7, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14 and 15.
Elsevier,
9th November 2020
In 2019, Dr. Ankur Patwardhan, Head of the Biodiversity Department at Maharashtra Education Society’s Abasaheb Garware College, Pune, India, was awarded the second prize in the Elsevier Foundation Green and Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. Contributing to SDGs 13 and 15, his project, “Butterfly attractant for pollination and ecosystem health”, focused on the plant-pollinator interactions that play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance and aimed at enhancing floral visits by butterflies through the development of natural attractant formulations. One year later, we interviewed Dr. Patwardhan about his experience at the Challenge, as well as the upcoming steps for his project.