Progress in Disaster Science, Volume 1, May 2019
The “build back better” (BBB) approach to disaster recovery was first introduced in 2006 by the United Nations Secretary-General's Special Envoy for Tsunami Recovery, former US President William Clinton. In 2015, BBB became the second half of Priority 4 of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030, in recognition of its widespread use and adoption among disaster risk management practitioners, policy-makers, and researchers.
Free Radical Biology and Medicine, Volume 135, 1 May 2019
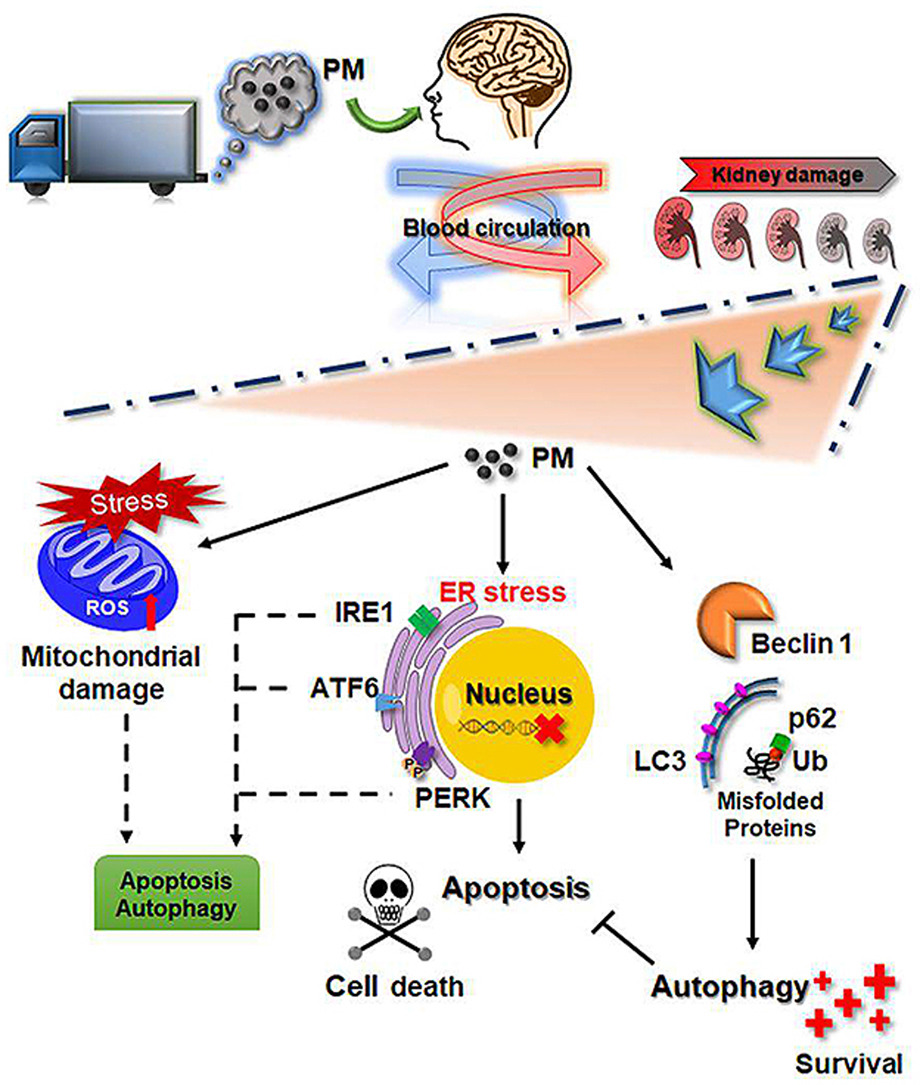
Traffic emission is responsible for most small-sized particulate matter (PM) air pollution in urban areas. Several recent studies have indicated that traffic-related PM may aggravate kidney disease. Furthermore, exposure to particulate air pollution may be related to the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been adequately addressed. In the present study, we studied the mechanisms of renal damage that might be associated with exposure to PM.