December 3rd is the International Day of People With Disabilities (IDPWD). In support of this year's theme - 'Not all Disabilities are Visible' - Elsevier presents presents a curated, open access collection of over 50 journal articles and book chapters focused on spreading awareness and understanding of disabilities, many of which are not immediately apparent. This includes mental illness, chronic pain or fatigue, brain injuries, neurological disorders, learning differences and cognitive dysfunctions, among others.
According to the WHO World Report on Disability, 15 per cent of the world’s population, or more than 1 billion people, are living with disability. Of this number, it’s estimated 450 million are living with a mental or neurological condition— and two-thirds of these people will not seek professional medical help, largely due to stigma, discrimination and neglect.
Another 69 million individuals are estimated to sustain Traumatic Brain Injuries each year worldwide, while one in 160 children are identified as on the autism spectrum.
These are just some examples of the millions of people currently living with a disability that is not immediately visible, and a reminder of the importance of removing barriers for all people living with disability, both visible and invisible.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, isolation, disconnect, disrupted routines and diminished services have greatly impacted the lives and mental well-being of people with disabilities right around the world. Spreading awareness of invisible disabilities, as well as these potentially detrimental impacts to mental health, is crucial as the world continues to fight against the virus.
Neuron, Volume 100, 24 October 2018
Recent progress in the genomics of non-syndromic autism spectrum disorder (nsASD) highlights rare, large-effect, germline, heterozygous de novo coding mutations. This distinguishes nsASD from later-onset psychiatric disorders where gene discovery efforts have predominantly yielded common alleles of small effect. These differences point to distinctive opportunities for clarifying the neurobiology of nsASD and developing novel treatments.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 120, March 2020
Smart home technologies refer to devices that provide some degree of digitally connected, automated, or enhanced services to building occupants. Smart homes have become central in recent technology and policy discussions about energy efficiency, climate change, and the sustainability of buildings. Nevertheless, do they truly promote sustainability goals? In addition, what sorts of benefits, risks, and policies do they entail?
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, Volume 62, September 2020
Objective imaging-based biomarker discovery for psychiatric conditions is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Using a machine learning framework, this work investigated the utility of brain's functional network topology (complex network features) extracted from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) functional connectivity (FC) as viable biomarker of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). To this end, we utilized resting-state fMRI data from the publicly available ABIDE dataset consisting of 432 ASD patients and 556 matched healthy controls.
Neuron, Volume 102, 3 April 2019
Perinatal depression (PND) is a heterogeneous disorder with differences in timing of onset of depression, which influences symptomology, severity, and treatment efficacy. Researchers must embrace the heterogeneity to bring fruition to a precision medicine approach for women in reproductive mental health care. Galea and Frokjaer discuss the heterogeneity of perinatal depression based on timing onset, which influences symptoms and has implications for etiology and treatment efficacy.
Neuron, Volume 102, 3 April 2019
There have been several recent studies addressing the genetic architecture of depression. This review serves to take stock of what is known now about the genetics of depression, how it has increased our knowledge and understanding of its mechanisms, and how the information and knowledge can be leveraged to improve the care of people affected.
Neuron, Volume 101, 20 March 2019
Altered synaptic structure and function is a major hallmark of fragile X syndrome (FXS), autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), and other intellectual disabilities (IDs), which are therefore classified as synaptopathies. FXS and ASDs, while clinically and genetically distinct, share significant comorbidity, suggesting that there may be a common molecular and/or cellular basis, presumably at the synapse.
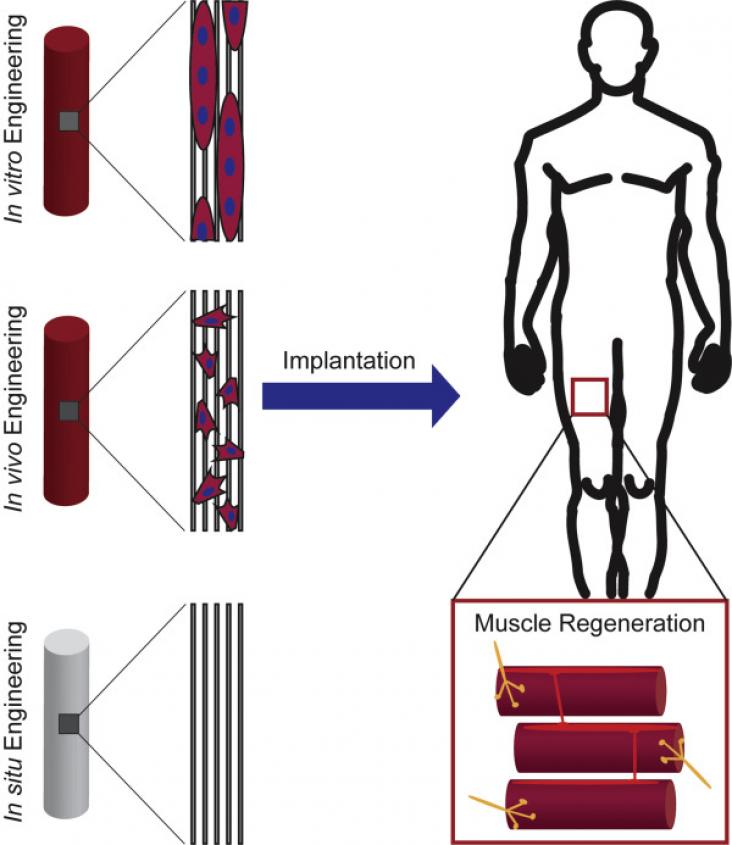
Active Above-Knee Prosthesis, A Guide to a Smart Prosthetic Leg, 2020, Pages 1-17
Assistive Technology for the Elderly, 2020, Pages 1-43
Advanced Rehabilitative Technology, Neural Interfaces and Devices, 2018, Pages 1-10
Improving Library Services to People with Disabilities, Chandos Information Professional Series, 2007, Pages 1-20
Improving Library Services to People with Disabilities, Chandos Information Professional Series, 2007, Pages 65-86
Epidemiology of Diabetes, 2019, Pages 45-55
Global Mental Health and Neuroethics, Global Mental Health in Practice, 2020, Pages 237-261
Rosenberg's Molecular and Genetic Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disease (Sixth Edition), Volume 1, 2020, Pages 199-207
Emerging Voices in Natural Hazards Research, 2019, Pages 327-356
Social Media: The Academic Library Perspective, Chandos Publishing Social Media Series, 2019, Pages 45-55
Multimodal Behavior Analysis in the Wild, Advances and Challenges, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, Pages 79-102
Assistive Technologies (Fifth Edition): Principles & Practice, 2020, Pages 16-30
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 48, 2015, Pages 1-9
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 48, 2015, Pages 43-72
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 55, 2018, Pages 145-180
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 55, 2018, Pages 213-266
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 54, 2018, Pages 71-104
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 54, 2018, Pages 177-209
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 52, 2017, Pages 37-74
International Review of Research in Developmental Disabilities, Volume 52, 2017, Pages 141-174