World Environment Day is the most renowned day for environmental action. Since 1974, it has been celebrated every year on June 5th, engaging governments, businesses, celebrities and citizens to focus their efforts on a pressing environmental issue.
To mark World Environment Day 2021, Elsevier presents a curated list of free access journal articles and book chapters in support of this year's theme - Ecosystem Restoration.
People and the planet are only as healthy as the ecosystems we all depend on. Bringing degraded ecosystems back to life – for example by planting trees, cleaning up riverbanks, or simply giving nature space to recover – increases their benefits to society and biodiversity. Without reviving ecosystems, we cannot achieve the Sustainable Development Goals or the Paris Climate Agreement. But ecosystems are also complex and highly varied, and their restoration needs careful planning and patient implementation.
World Environment Day 2021 also marks the launch of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, a rallying call for the protection and revival of ecosystems all around the world, for the benefit of people and nature. The UN Decade runs from 2021 through 2030, which is also the deadline for the Sustainable Development Goals and the timeline scientists have identified as the last chance to prevent catastrophic climate change. It aims to halt the degradation of ecosystems, and restore them to achieve global goals. Only with healthy ecosystems can we enhance people’s livelihoods, counteract climate change, and stop the collapse of biodiversity.
Trends in Food Science and Technology, Volume 107, January 2021
Background: Today's meat and dairy industry has a vast environmental footprint. To reach the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs) of ending hunger globally (SDG #2) and achieving sustainable consumption and production (SDG #12), this food production system needs to change. Recent years have seen the rise in popularity of the vegan or plant-based diet among consumers, which can go some way to reducing the environmental burden.
International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, Volume 24, July 2021
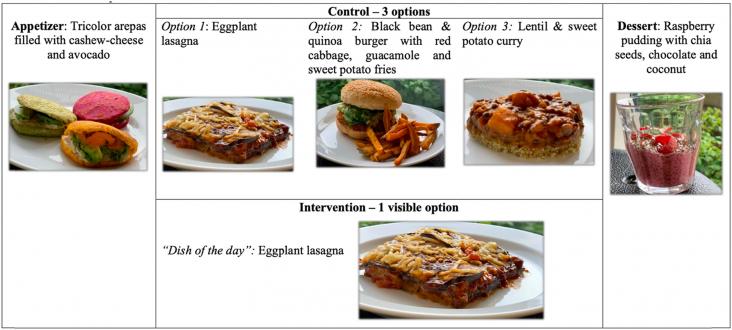
A nudge experiment was performed to evaluate the effectiveness of presenting a menu with the dish-of-the-day (DoD) vs. a menu with free choice to facilitate consumer choice towards a fully plant-based, nutritious and tasty meal in foodservice setting. A menu card in control condition included the appetizer, the three mains and a dessert. The menu card in the intervention included the appetizer, eggplant lasagne as the DoD, and the dessert. Thirty-three volunteers ate twice at Future Consumer Lab in Copenhagen, once in each condition (67% women; mean age 25y; SD2.1).
Scientific African, Volume 7, March 2020
Increased demand for food to feed the ever-growing population led to development and adoption of synthetic chemicals as a quick and effective strategy of managing crop pests and diseases. However, overreliance on synthetic pesticides is discouraged due to their detrimental effects on human health, the environment, and development of resistant pest and pathogen strains. This, coupled with increasing demand for organically produced foods, stimulated search for alternative approaches and botanical pesticides are particularly gaining importance.
She Ji, Volume 5, Spring 2019
There is a metabolic rift running through our economy and culture, and it is distracting our attention from care for the biosphere. To heal this rift, the diverse groups of people that make up humankind need a shared purpose that everyone can relate to and support. A strong candidate for that shared purpose is care for the bioregion—bioregioning—as an activity that creates value.
Resources Policy, Volume 74, December 2021
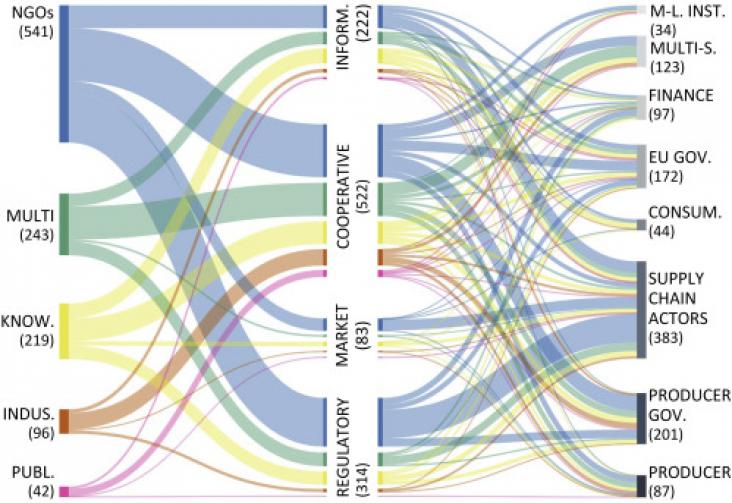
With the rapid development of China's economy, it has become crucial to achieve the right balance between economic development and environmental protection. Green growth is a significant approach to addressing the relationship between economic development and the environment. Low-carbon development and ecological protection are two essential aspects of green development, and they tremendously impact enterprises' resource-based supply chain. Hence, this paper seeks to explore the revenue distribution mechanism of the resource-based supply chain in the context of green development.
International Economics, Volume 134, August 2013
The economic crises seems blinding the governments and major economic actors toward environmental troubles. Nevertheless, the impacts of population growth and economic expansion have now the potential to disrupt important regulatory functions of global ecological systems. Green growth involves transforming the production and consumption processes in order to maintain or restore these regulatory functions of the planet's natural capital. It requires that environmental facto rs be treated as an essential factor of production and not merely an externality.
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 29, June 2021
Microplastic pollution has sparked interest from researchers, public, industries, and regulators owing to reports of extensive presence of microplastics in the environment, household dust, drinking water, and food, which indicates chronic exposure to organisms within ecosystems and in human living spaces. Although exposure to microplastics is evident, negative effects from microplastics appear to be minimal in most studies on biota, and no risk assessments have been completed for microplastics on human health.
Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 66, March 2021
The climate emergency and population growth are challenging water security and sustainable urban design in cities worldwide. Sustainable urban development is crucial to minimise pressures on the natural environment and on existing urban infrastructure systems, including water, energy, and land. These pressures are particularly evident in London, which is considered highly vulnerable to water shortages and floods and where there has been a historical shortage of housing. However, the impacts of urban growth on environmental management and protection are complex and difficult to evaluate.
Sustainable Cities and Society, Volume 66, March 2021
Electric vehicles (EVs) are widely regarded as the key to finally making private mobility clean, yet virtually no research is being conducted on their potential contribution to the expansion of impervious surfaces. This study aims to start a discussion on the topic by exploring three relevant issues: the impact of EVs’ operating costs on urban size, the space requirements of charging facilities, the land demand of energy production through renewables.
Food Webs, Volume 24, September 2020
Ecology plays a central role in the management and conservation of ecosystems. However, as coral restoration emerges as an increasingly popular method of confronting the global decline of tropical coral reefs, an ecological basis to guide restoration remains under-developed. Here, we examine potential contributions that trophic ecology can make to reef restoration efforts. To do so, we conducted a comprehensive review of 519 peer-reviewed restoration studies from the past thirty years.
Environment International, Volume 134, January 2020
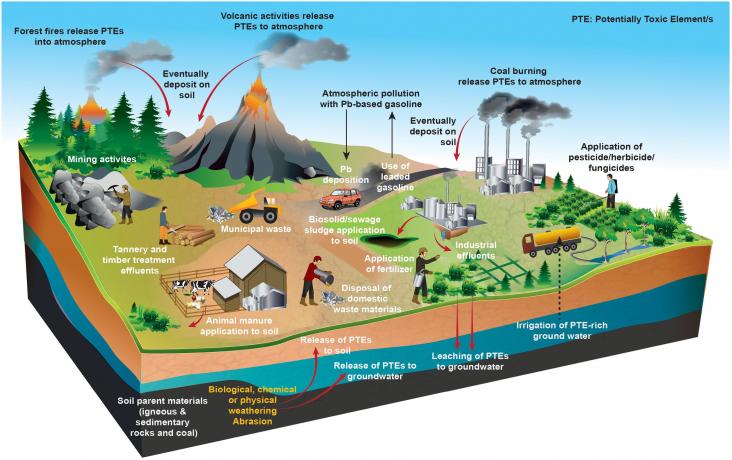
Mercury contamination in soil, water and air is associated with potential toxicity to humans and ecosystems. Industrial activities such as coal combustion have led to increased mercury (Hg) concentrations in different environmental media. This review critically evaluates recent developments in technological approaches for the remediation of Hg contaminated soil, water and air, with a focus on emerging materials and innovative technologies.
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 2, March 2021
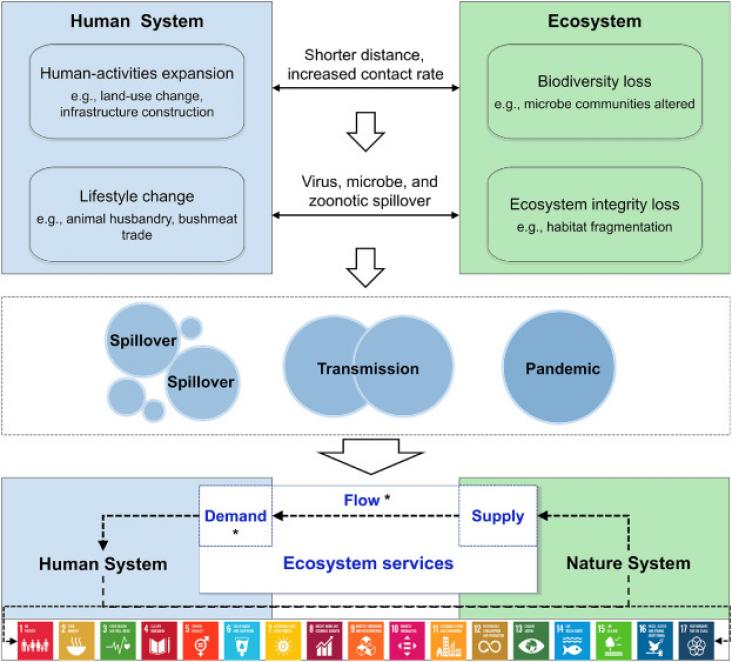
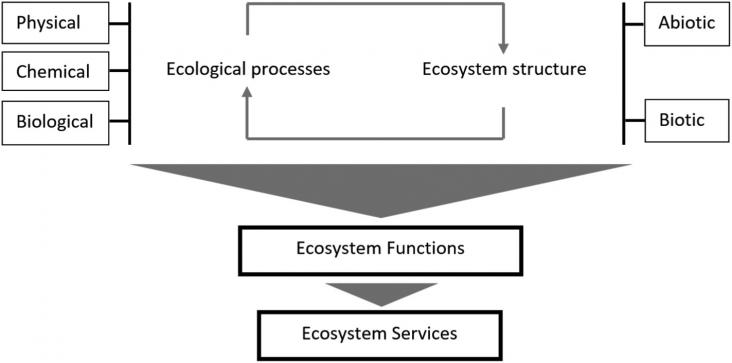
The COVID-19 pandemic has stalled and rolled back progress on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Ecosystem services (ESs), defined as the contributions of ecosystems to human well-being, underpin the achievement of SDGs. To promote SDG achievement in post-pandemic era, we teased out the links between ESs and SDGs while examining the impact of COVID-19. We found that ESs benefited all SDGs, yet man-made pressures led to degradation of ecosystems and their services. There is broad consensus that the virus lurks in degraded ecosystems and generates spillover due to human interference.
iScience, Volume 24, 19 March 2021
Proximity and size of the nearest market (‘market gravity’) have been shown to have strong negative effects on coral reef fish communities that can be mitigated by the establishment of closed areas. However, moray eels are functionally unique predators that are generally not subject to targeted fishing and should therefore not directly be affected by these factors. We used baited remote underwater video systems to investigate associations between morays and anthropogenic, habitat, and ecological factors in the Caribbean region.
iScience, Volume 24, 19 March 2021
iScience, Volume 24, 19 March 2021
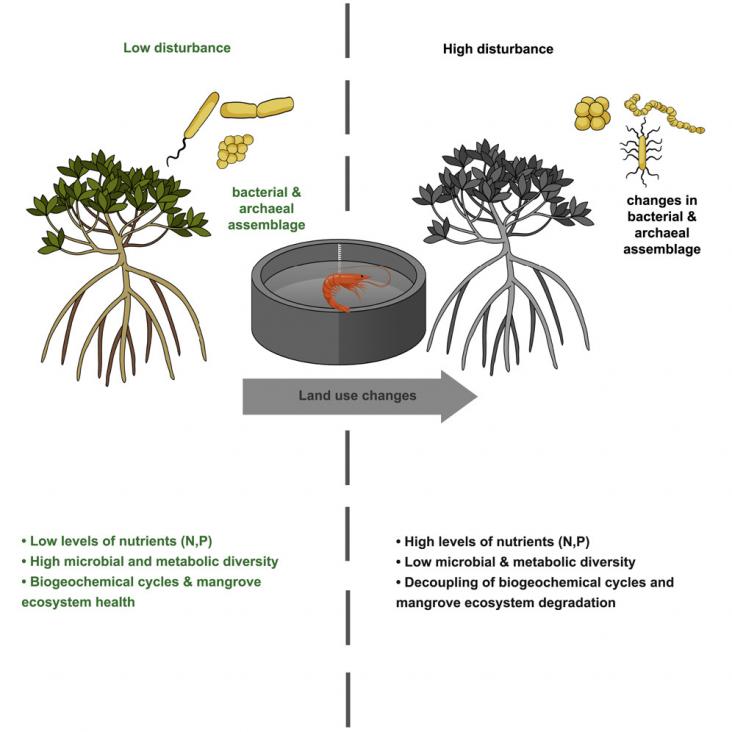
Mangrove-dominated estuaries host a diverse microbial assemblage that facilitates nutrient and carbon conversions and could play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem health. In this study, we used 16S rRNA gene analysis, metabolic inference, nutrient concentrations, and δ13C and δ15N isotopes to evaluate the impact of land use change on near-shore biogeochemical cycles and microbial community structures within mangrove-dominated estuaries.
Cities, Volume 26, August 2009
Urban forests are integral components of urban ecosystems, which could generate significant ecosystem services, such as offsetting carbon emission, removing air pollutants, regulating the microclimate, and recreation. These ecosystem services contribute to improving environmental quality, quality of life, and sustainable urban development. Despite a long history of inserting vegetation in human settlements in China, modern scientific study of this natural-cum-cultural resource did not start until the 1990s.
One Earth, Volume 2, 22 May 2020
Mangrove forests are found on sheltered coastlines in tropical, subtropical, and some warm temperate regions. These forests support unique biodiversity and provide a range of benefits to coastal communities, but as a result of large-scale conversion for aquaculture, agriculture, and urbanization, mangroves are considered increasingly threatened ecosystems.
One Earth, Volume 2, 19 June 2020
Protecting the ocean has become a major goal of international policy as human activities increasingly endanger the integrity of the ocean ecosystem, often summarized as “ocean health.” By and large, efforts to protect the ocean have failed because, among other things, (1) the underlying socio-ecological pathways have not been properly considered, and (2) the concept of ocean health has been ill defined. Collectively, this prevents an adequate societal response as to how ocean ecosystems and their vital functions for human societies can be protected and restored.
One Earth, Volume 4, 22 January 2021
Maintaining or restoring connectivity among wildlife populations is a primary strategy to overcome the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation. Yet, current connectivity planning efforts typically assess landscape resistance, the ability of organisms to cross various biophysical elements in a landscape, while overlooking the various ways in which human behaviors influence connectivity. Here, we introduce the concept of “anthropogenic resistance” to capture the impacts of human behaviors on species' movement through a landscape.
Cities, Volume 113, June 2021
This paper aims to contribute to the limited understanding and recognition of soil ecosystem services (SoES) in spatial planning. In light of its critical role in climate crises and due to its global degradation, soil has drawn considerable attention in the recent global agenda. As one of its vital services, soil serves as a terrestrial carbon pool, which significantly contributes to offset greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere (EEA, 2012).
One Earth, Volume 2, Issue 1, 2020, Pages 98-108
The Journal of Climate Change and Health, Volume 2, May 2021, 100011
Future Foods, Volume 3, June 2021
Food is essential to provide energy for human cellular metabolism, and is usually made from plants or animals. Beside plants and animals, other important food sources are made by microorganisms, typically products of fermentation (e.g bread, wine, beer, soy sauce, etc). Nowadays, because of the increasing environmental pollution, climate change and population growth, is becoming challenging to keep the food supply safe, nutritious and sustainable. Importantly, the development of the synthetic biology field enable the engineering of cells that can be used in food manufacturing.
Food Quality and Preference, Volume 93, October 2021
In view of all kinds of sustainability concerns related to our current diet, it is essential to gain a good understanding of the sustainability motives consumers have for selecting their food. A comprehensive and validated scale to measure sustainability motives within the full range of food choice motives could contribute to this understanding, especially as sustainability is a multi-faceted concept in which the different aspects can sometimes be conflicting.
Materials and the Environment, Third Edition: Chapter 11 - Renewable materials, natural materials, Volume , 2021
Encyclopedia of Renewable and Sustainable Materials: Nanomaterial for CO2 Sequestration, Volume 3, 2020
Soil Health and Intensification of Agroecosystems, Volume , 22 March 2017
Methods in Stream Ecology: Third Edition, Volume 1, 20 February 2017
Methods in Stream Ecology: Third Edition, Volume 1, 20 February 2017
Land Restoration: Reclaiming Landscapes for a Sustainable Future, Volume , 2016
Aquatic Ecotoxicology: Advancing Tools for Dealing with Emerging Risks, Volume , July 13, 2015
Aquatic Ecotoxicology: Advancing Tools for Dealing with Emerging Risks, July 13, 2015
Coastal Wetlands: An Integrated Ecosystem Approach, 1 January 2018
Encyclopedia of Modern Optics, Volume 1-5, 1 January 2018
World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation Volume II: The Indian Ocean to the Pacific, Volume , 1 January 2018
Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design: Potential, Design, Ecological Health, Urban Greening, Economics, Policies, and Community Perceptions, Volume , 1 January 2018
Coastal Wetlands: An Integrated Ecosystem Approach, Volume , 1 January 2018
Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, Volume , 1 January 2019
The pollution of the marine environment by solid wastes, either directly introduced into the sea or discharged into the oceans from rivers or pipelines, is considered from the perspective of both their impacts and their regulation. The waste materials covered include dredged material, particulate wastes from sand/gravel extraction, and land reclamation, and industrial wastes including mining wastes, munitions, and plastics/litter.
Coasts and Estuaries: The Future, Volume , 31 January 2019
Bivalve habitats were once a dominant ecosystem in temperate and subtropical estuaries worldwide. While bivalve habitats are greatly reduced from their former abundance, remnant, and restored populations have been shown to provide a suite of important ecosystems services including improving water quality, coastal protection, and providing fisheries nursery habitat, in addition to providing a direct food value.
Advances in Ecological Research, Volume 64, January 2021
Global social and economic changes, alongside climate change, are affecting the operating environment for agriculture, leading to efforts to increase production and yields, typically through the use of agrochemicals like pesticides and fertilizers, expanded irrigation, and changes in seed varieties. Intensification, alongside the expansion of agriculture into new areas, has increased harvest, but has also had numerous well-known impacts on the environment, ultimately resulting in a loss of resilience and lack of sustainability in agro-ecosystems.
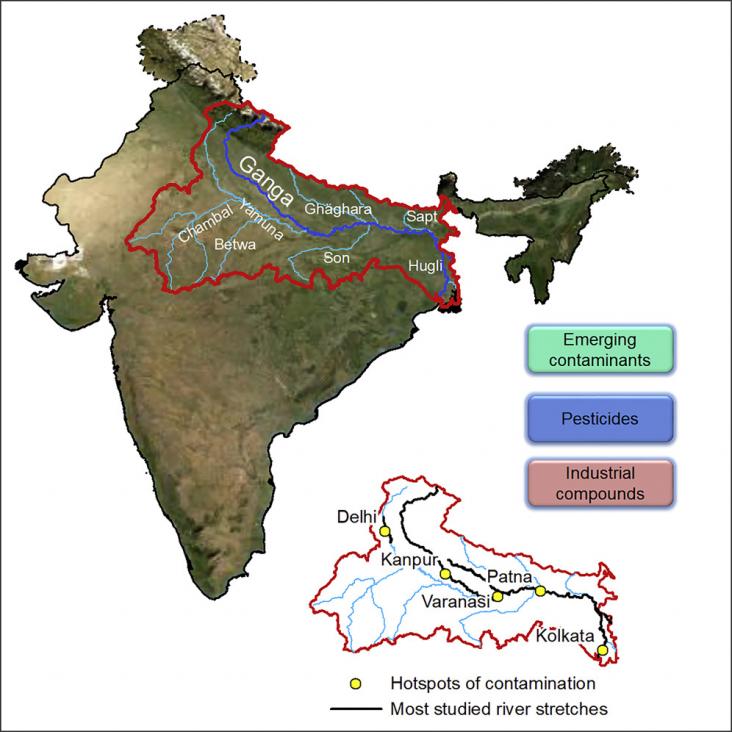
Management of Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CEC) in Environment, 2021.
Management of Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CEC) in Environment, 2021.
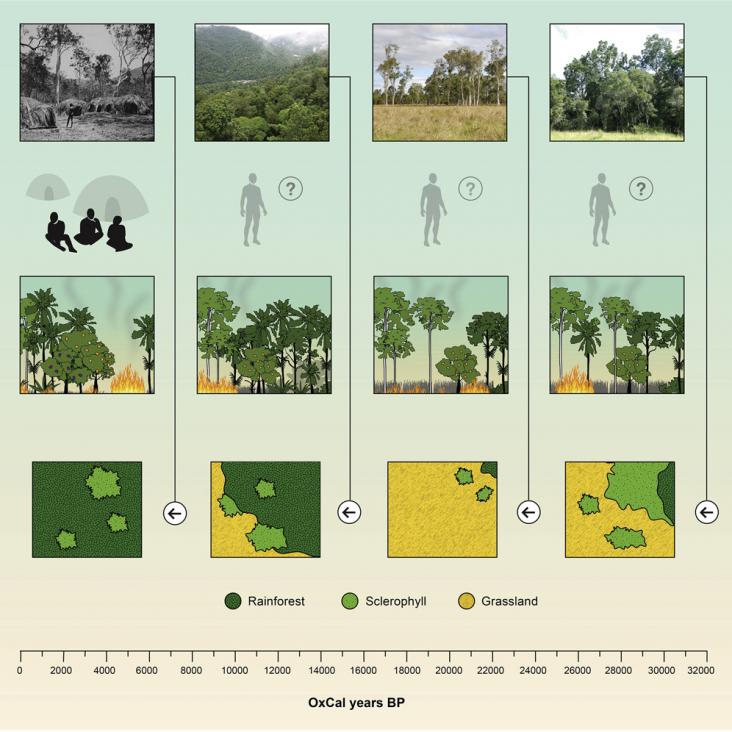
Encyclopedia of the World's Biomes, 2020.
Encyclopedia of the World's Biomes, 2020.
Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, 2021.
Handbook of Water Purity and Quality, Second Edition, 2021.
Wood Microbiology, Second Edition, 2020.
Developments in Soil Science, Volume 36, 2019.
Handbook of Bioremediation, 2021.
Dynamic Sedimentary Environments of Mangrove Coasts, 2021.
Soils and Landscape Restoration, 2021.
An Introduction to Aquatic Toxicology, 2014.
Advances in Ecological Research, Volume 64, January 2021
Foundations for Sustainability, A Coherent Framework of Life-Environment Relations, 2019, Pages 205-230
Foundations for Sustainability, A Coherent Framework of Life-Environment Relations, 2019, Pages 1-25